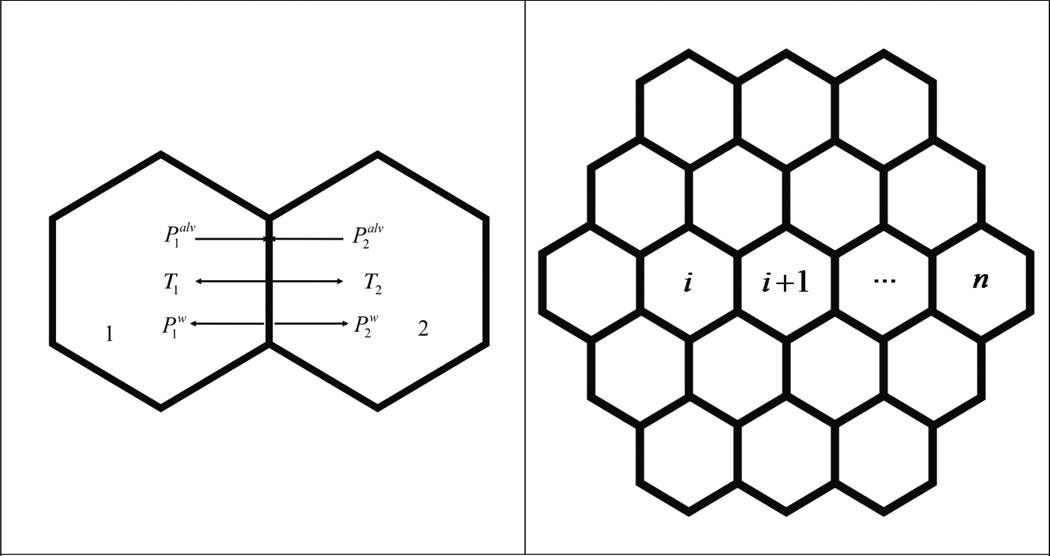
Fig. 1.
(a) Stresses normal to the wall shared by two adjacent alveoli. Palv is the alveolar pressure and Pw comes from the surface tension of the liquid membrane that defines the boundary of alveolus. T is the recoil stress from the resistance of the alveolar wall against the deflation or inflation of the alveolus inside.
(b): Arrangement of alveoli on a 2D plane.