Figure 2. Biochemical structure of α-synuclein and its pathological distribution in Parkinson's disease and a mouse model of Lewy body disease.
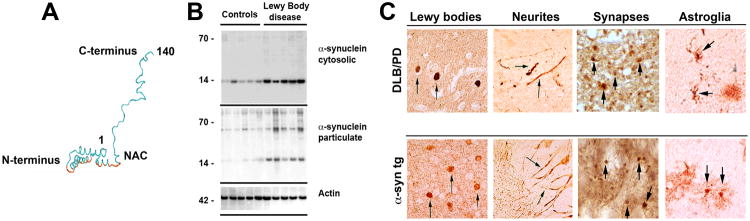
a | Computer-generated model of α-synuclein (α-syn) representing the N-terminal α helices, non-amyloid-β component of Alzheimer's disease amyloid plaques (NAC; depicted in red), and unstructured C-terminal regions. b | Western blot identifying α-syn in brain homogenates from control and Lewy body disease cases that were divided into cytosolic and particulate fractions. α-Syn migrated to 57–60 kDa as well as to 14 kDa in the particulate but not cytosolic fraction due to the different conformational states of the protein. c, d | α-Syn is present in Lewy bodies, neurites, synapses and astroglia in dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Parkinson's disease (PD) and in PDGFβ-human α-syn wild type transgenic mice, as indicated by arrows.
