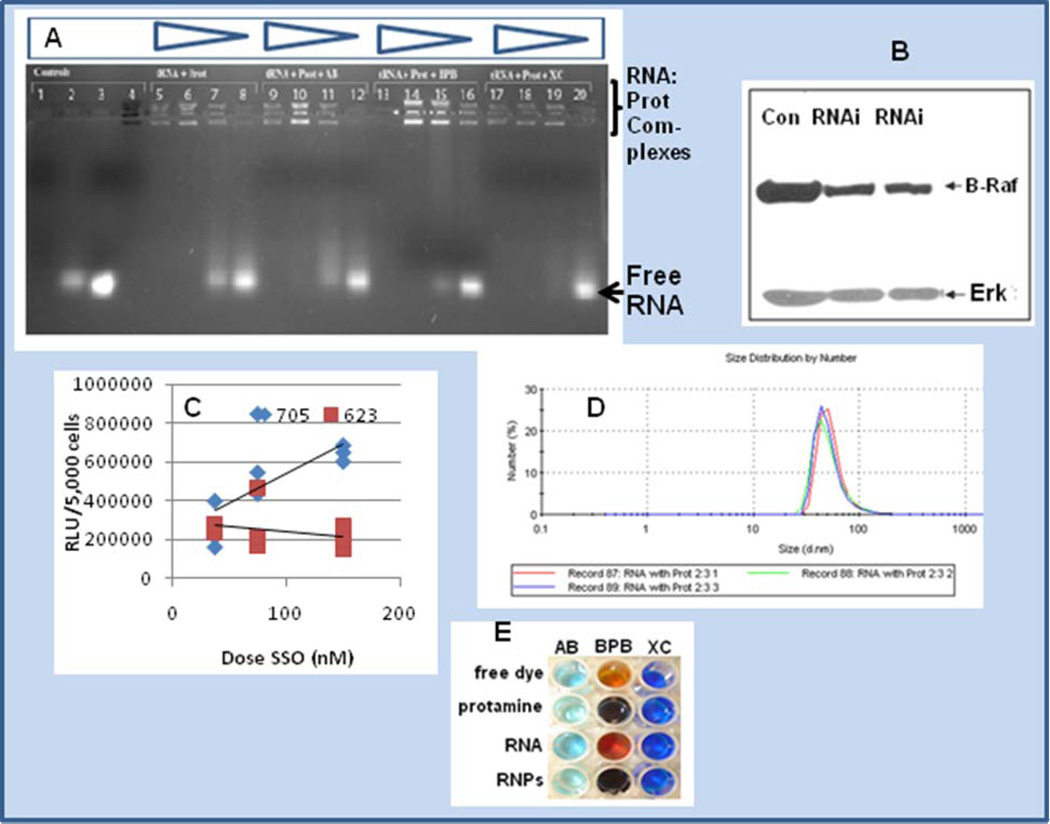
Fig. 5.
Panel A is a gel shift experiment of RNA:protamine in the presence of amido black, bromophenol blue and xylene cyanol. Staining of the multiple isoforms of protamine is shown in lane 4 containing amido black. Staining of the protamine:RNA complex in decreasing quantities of protamine is shown in lanes 5–8 (left to right, 0.5 mg/ml , 0.1 mg/ml, 0.05 mg/ml and 0.03 mg/ml). Lanes 9–12, 13–16, and 17–20 represent a matched set compared to lanes 5–8 with the inclusion of dyes amido black (lanes 9–12), bromophenol blue (lanes 13–16) or xylene cyanol (lanes 17–20), respectively. Panel B is a western blot of A375 human melanoma cells treated for 48 hrs with siRNA delivered as a protamine complex (RNAi lanes) or untreated controls (Con). Inhibition is shown, and Erk is blotted as a comparator. Panel C is a dose response experiment comparing SSO 705 and SSO 623 sequences for their ability to splice-site switch and up-regulate luciferase expression in the HeLa 705 pLuc system [3, 22, 33]. Panel D represents protamine-RNA complexes of approximate 50 nm size (n = 3 runs), where complexes were formed with vol/vol addition of protamine (1 mg/ml) and tRNA (0.1 mg/ml). Panel E represents chromophoric shift of amido black (AB), bromophenol blue (BPB) and xylene cyanol (XC) in the absence or presence of RNPs (RNA:protamine nanoparticles).