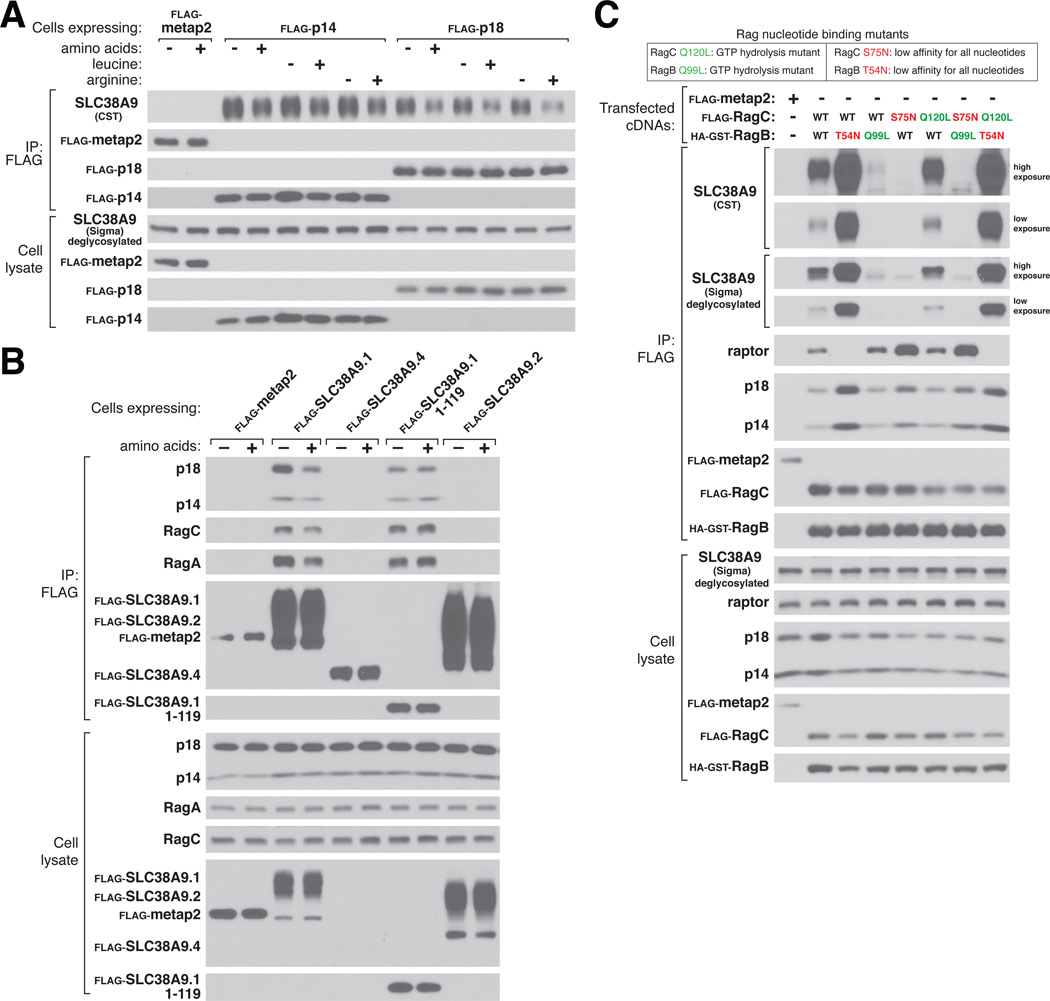
Figure 4.
Modulation of the interaction between SLC38A9 and Ragulator and the Rag GTPases by amino acids. (A) Effects of amino acids on interaction between the Ragulator complex and endogenous SLC38A9. HEK-293T cells stably expressing the indicated FLAG-tagged Ragulator components were deprived of total amino acids, leucine, or arginine for 1 hour and, where indicated, re-stimulated with amino acids, leucine, or arginine for 15 min. After lysis, samples were subject to FLAG immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting for the indicated proteins. Quantification of SLC38A9 levels in the stimulated state relative to starved state, p14 IP: 0.75 (+AA), 0.79 (+L), 0.74 (+R); p18 IP: 0.56 (+AA), 0.57 (+L), 0.49 (+R). (B) Effects of amino acids on the interaction between full-length or truncated SLC38A9.1 and endogenous Ragulator and the Rag GTPases. Experiment was performed as in (A) except that cells stably expressed the indicated SLC38A9 isoforms or its N-terminal domain (SLC38A9.1 1-119). Quantification of indicated protein levels in the stimulated state relative to starved state, SLC38A9.1 IP: 0.43 (p18), 0.51 (p14), 0.61 (RagC), 0.58 (RagA); SLC38A9.1 1-119 IP: 0.99 (p18), 1.05 (p14), 1.04 (RagC), 1.09 (RagA). (C) Effects of the RagBT54N mutation on association with endogenous SLC38A9. HEK-293T cells were transfected with the indicated cDNAs in expression vectors and lysates were prepared and subjected to FLAG immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting for the indicated proteins. Two different antibodies were used to detect endogenous SLC38A9.