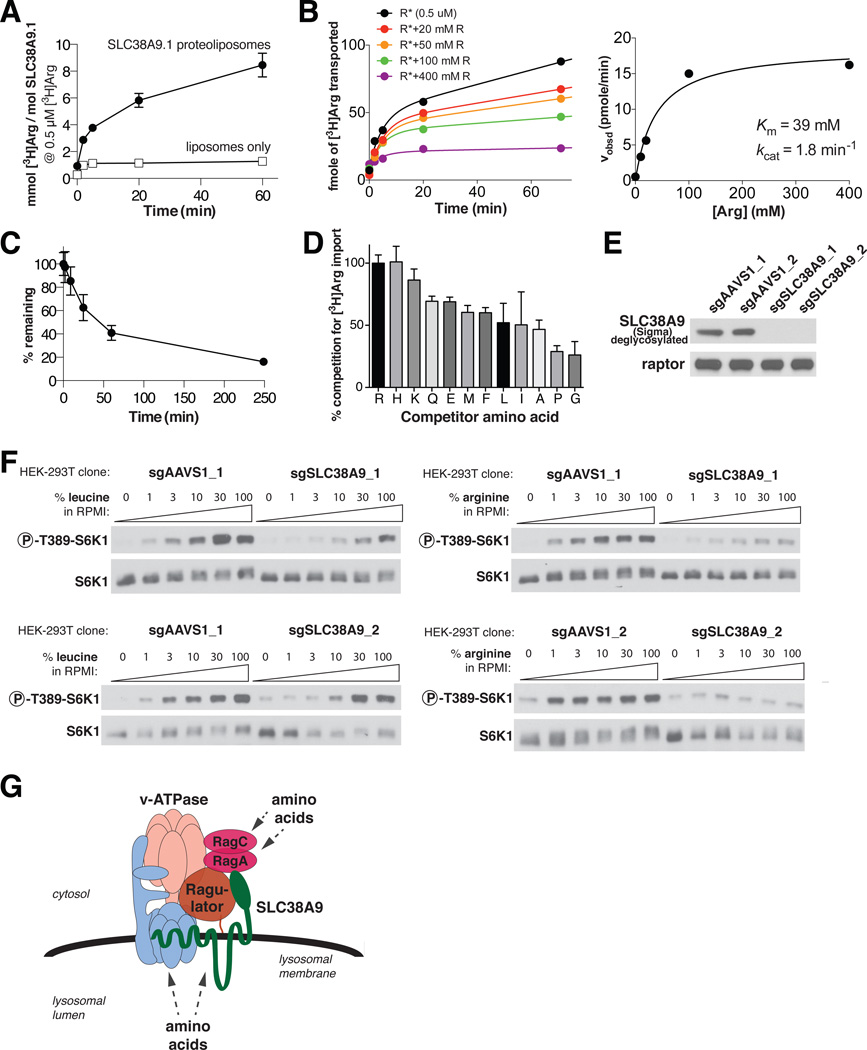
Figure 5.
SLC38A9.1 is a low affinity amino acid transporter and is necessary for mTORC1 pathway activation by arginine. (A) Time-dependent uptake of [3H]arginine at 0.5 μM by proteoliposomes containing 22.4 pmol of SLC38A9.1. To recapitulate the pH gradient across the lysosomal membrane, the lumen of the proteoliposomes is buffered at pH 5.0, while the external buffer is pH 7.4. (B) Steady-state kinetic analysis of SLC38A9.1 uptake activity reveals a Michaelis constant (Km) of ~39mM and catalytic rate constant (kcat) of ~1.8min−1. (Left) Time course of [3H]arginine (R*) uptake, given fixed [3H]arginine (0.5 μM) and increasing concentrations of unlabeled arginine. (Right) Velocity, calculated from left panel, as a function of total arginine concentration. Data were fitted to the Michaelis-Menton equation. Experiment was repeated over 4 times with similar results and a representative one is shown. (C) Time-dependent efflux of SLC38A9.1 proteoliposomes following 1.5 hr loading with 0.5 μM [3H]arginine. (D) Competition of 0.5 μM [3H]arginine transport by SLC38A9.1 using 100 mM of indicated unlabeled amino acids. In A-D, error bars represent standard deviation derived from at least 3 measurements. (E) HEK-293T cells null for SLC38A9 were generated using CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing using two different guide sequences and isolated by single cell cloning. The AAVS1 locus was targeted as a negative control. (F) Impairment of arginine-induced activation of the mTORC1 pathway in SLC38A9-null HEK-293T cells. Cells were starved of the indicated amino acid for 50 minutes and stimulated for 10 minutes using the indicated amino acid concentrations. The leucine and arginine concentrations in RPMI are, respectively, 381 μM and 1.14 mM. (G) Model for distinct amino acid inputs to the Rag GTPases in signaling amino acid sufficiency to mTORC1.