Figure 4. Angiogenic molecules involve in focal angiogenesis.
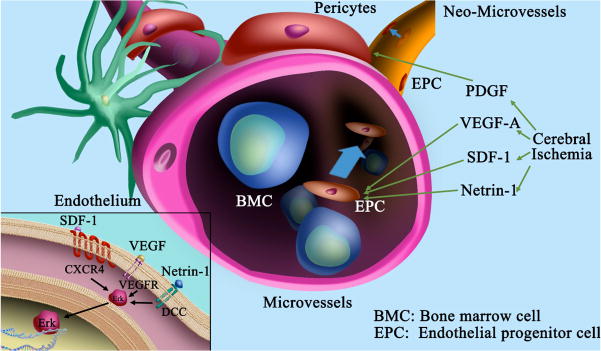
Schematic representation shows the function of angiogenic molecules during cerebral ischemia. Injured neurons and activated astrocytes and endothelial cells express growth factors such as VEGF, PDGF, MMPs and etc., which degrade basement membrane, activate endothelial cells and induce sprout. Bone marrow cells (BMCs) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) are homing towards the sprout regions via chemokines CXCL12/SDF-1 and netrin-1, leading to tube formation. Lower left inset indicates that VEGF signals through VEGF-R1 or VEGF-R2, CXCL12/SDF-1 through CXCR4 or CXCR7, and Netrin-1 through DCC or UNC5H2 receptors, all of which further activate ERK signaling pathway and induce downstream cascade activation.
