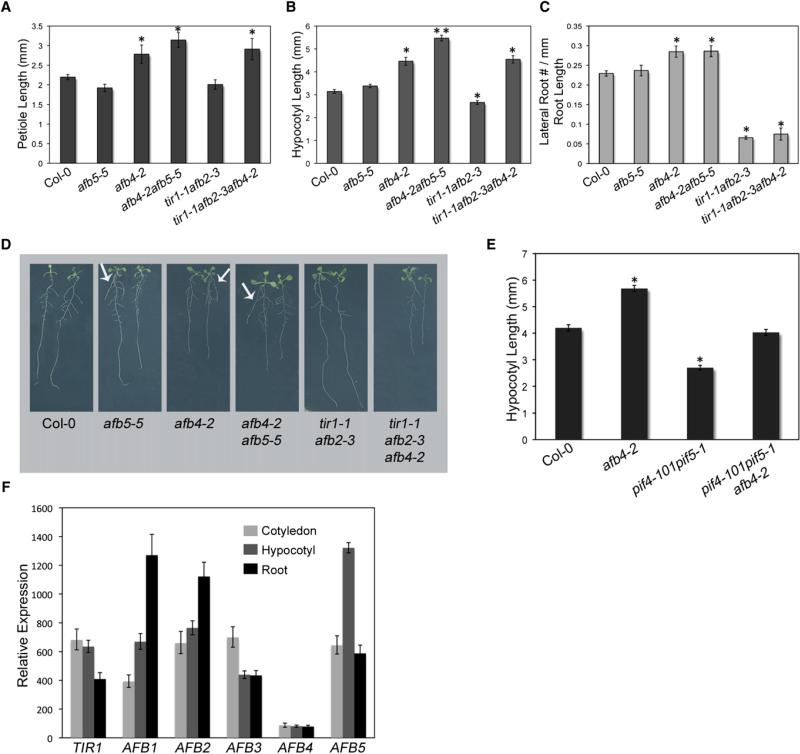
Figure 3. The afb4-2 Mutant Shows Stronger Auxin-Related Phenotypes Than afb5-5 and Has Much Lower Expression Levels.
(A and B) Petiole (A) and hypocotyl (B) lengths of 6-day-old WT and tir1/afb mutant seedlings.
(C) Lateral root number divided by primary root length (mm) in 10-day-old WT and tir1/afb mutant seedlings grown under long-day (LD) photoperiods (16 hr light:8 hr dark). Measurement values are shown in Figure S2F.
(D) Images of 7-day-old WT and tir1/afb mutant seedlings grown under LD photoperiods. Arrows point to lateral roots emerging from root-shoot junction.
(E) Hypocotyl lengths of 6-day-old WT and mutant seedlings grown at 22°C.
(F) qRT-PCR of TIR1, AFB4, and AFB5 in hypocotyl tissue from 4-day-old WT seedlings grown under short-day (SD) conditions.
Error bars represent standard error. *p < 0.05 versus WT, **p < 0.05 versus WT and other single and double mutants by Student's t test. See also Figure S2.