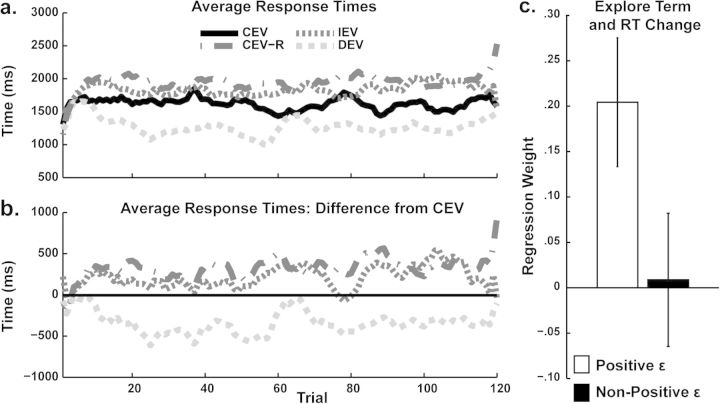
Figure 4.
Average RT performance. (a, b) Participants learned to adapt RTs (smoothed with a 5-point kernel) depending on block-specific reward structure. For example, participants responded slower when EV increased over time and they responded faster when EV decreased over time, even relative to their own performance when EV was constant. Slower RTs to the constant EV-reversed (CEV-R) condition demonstrate a preference for reward probability over magnitude (risk aversion). (c) Positive ϵ participants were characterized by the model as using relative uncertainty to guide exploration. Here it can be seen that this group was characterized by significant correlations between trial-to-trial measures of exploration and RT change.