Figure 3.
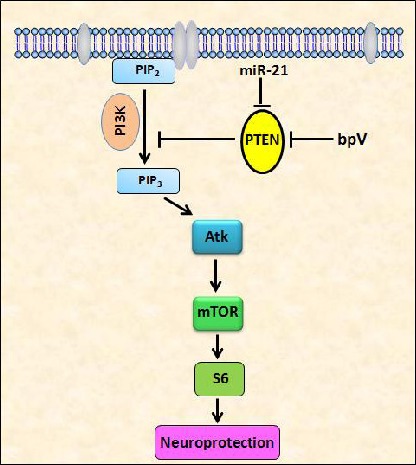
Schematic drawing shows PTEN-Akt/mTOR singling pathway in SCI.
PTEN's phosphatase converts phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3) into phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2), thus inhibiting downstream Akt and mTOR signaling.
PI3K converts PIP2 into PIP3, which can then activate Akt and mTOR, thus enhancing p-S6 expression leading to neuroprotection. Bisperoxovanadium (bpV) and miR-21 may induce Akt/mTOR activation by inhibition of PTEN, finally exert neuroprotective effects.
PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; SCI: spinal cord injury; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinases; S6: ribosomal protein S6.
