Figure 6.
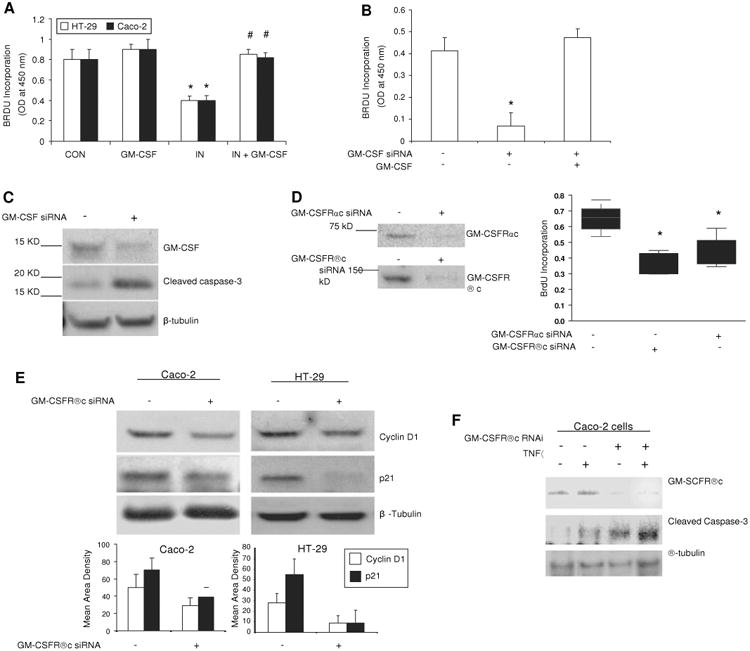
Granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) regulates survival and proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells in vitro. (A) Subconfluent Caco-2 and HT-29 cells were incubated with rhGM-CSF (1 ng/ml) and indomethacin (IN, 10-4 M) for 24 h, cell proliferation was measured using BrdU incorporation. *p<0.01 vs control (CON) group; #p<0.01 vs IN group (n=10). (B, C) gm-csf siRNA was used to knock down the expression of GM-CSF in subconfluent Caco-2 cells in the absence and presence of rhGM-CSF (1 ng/ml) administration for 24 h. Proliferation of Caco-2 cells was detected by BrdU incorporation and apoptosis of Caco-2 cells by cleaved caspase-3 western blot analysis. Control (CON) group: transfection reagent without siRNA; *p<0.05 vs control or GM-CSF group (n=10). (D) Proliferation of Caco-2 cells was detected under gm-csfαc or βc knockdown. *p<0.01 vs control group (n=10). Percentage of knock-down was determined by western blot analysis. (E) Cyclin D1 and p21 were determined by western blot analysis in subconfluent Caco-2 and HT-29 cells with and without gm-csfrβc knock-down. (F) After 24 h tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) (10 ng/ml) administration, cleaved caspase-3 was measured by western blot analysis in subconfluent Caco-2 cells with and without gm-csfrβc knock-down. Results representative of five independent experiments are shown. BrdU incorporation results are shown as mean±SEM.
