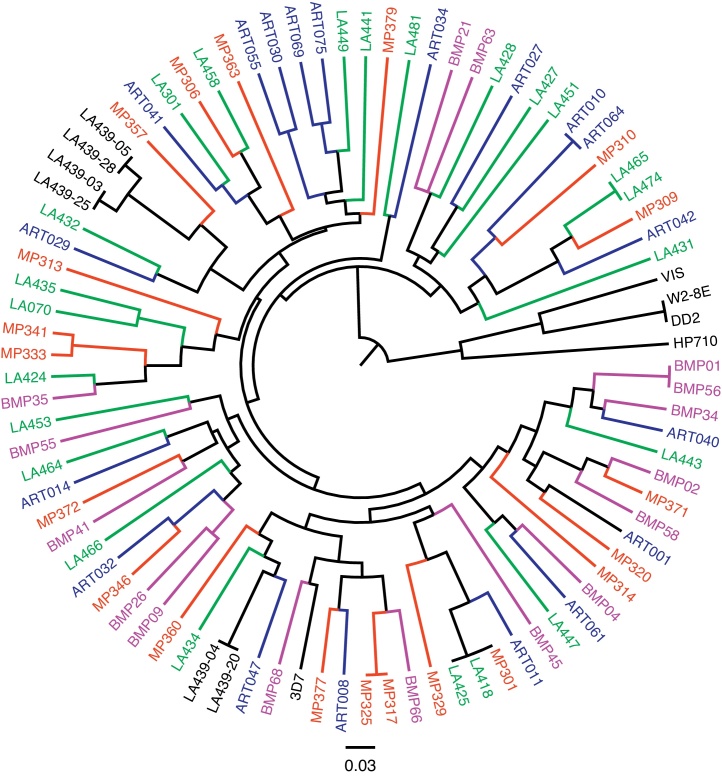
Fig. 1.
UPGMA tree showing relationships amongst 78 single-genotype infections and genotyping controls. The tree is constructed from a pairwise distance matrix, 1-ps, where ps is the proportion of SNP alleles shared between any two parasite isolates. Single-genotype infections sampled during each of the 4 years are coded using different colours (red = 2006, blue = 2007, green = 2008, purple = 2012) while laboratory controls are coded in black. Laboratory controls LA439-05, LA439-28, LA439-03, LA439-25, LA439-04 and LA439-20 are parasite clones isolated from a multiple-genotype infection sampled from Ndirande health centre in 2008. These were previously identified to be genetically identical using the 384-SNP assay (Nkhoma et al., 2012). LA439-05 and LA439-28, LA439-03 and LA439-25, LA439-04 and LA439-20 cluster together on the tree and are identical at all 24 SNPs genotyped. This result provides reassurance that the 24-SNP assay has enough resolution power for identifying both unique and identical parasite genotypes. Patients MP301, LA418 and LA425 had identical barcodes. Similarly, patients MP317 and MP325, ART010 and ART064, LA465 and LA474 had the same barcodes, indicating that they were infected with identical parasite genotypes.