Figure 3.
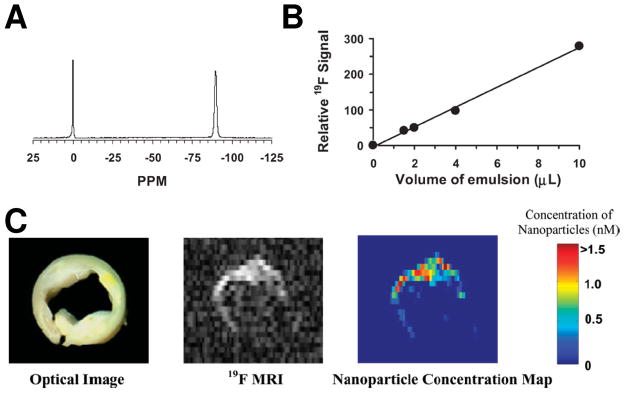
(A) A representative 19F spectrum of PFPE nanoparticle emulsion (−90 ppm) and trichlorofluormethane reference standard (0 ppm) acquired at 4.7 T. (B) The calibration curve for PFPE nanoparticle emulsion shows a linear relationship between the quantity of PFC nanoparticles and 19F signal intensity. (C) Left: An optical image of a human carotid endarterectomy sample shows moderate luminal narrowing and several atherosclerotic lesions. Middle: A 19F projection image acquired through the entire thickness of carotid artery sample shows high 19F signal along the lumen because of the binding of nanoparticles to fibrin. Right: The calculated concentration map of bound nanoparticles in the carotid sample based on 19F signal intensity in each voxel and the calibrated standard curve in (B). (From Morawski et al. [1].)
