Figure 3.
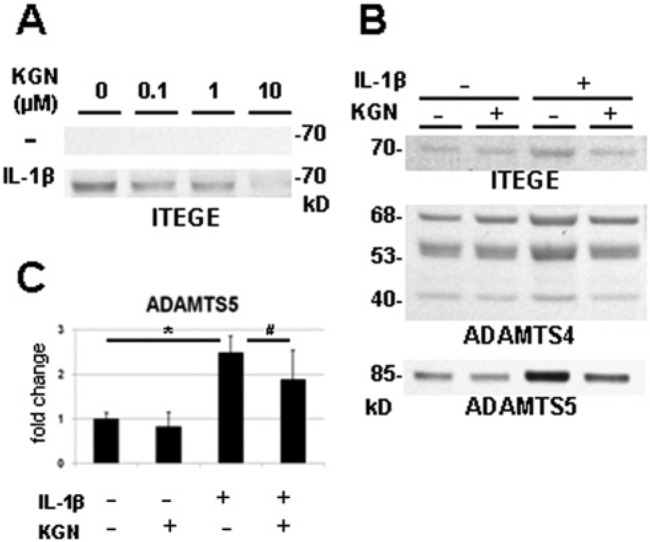
Kartogenin treatment reduces IL-1β stimulation of the release of G1-ITEGE and ADAMTS5 into the media of articular chondrocyte cultures. Human articular chondrocytes were cultured in monolayer in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 10 ng/ml IL-1β and treated with 0 to 10 µM kartogenin (KGN) for 48 hours (A). Bovine articular chondrocytes were cultured with (+) or without (−) 1 ng/mL IL-1β in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 10 µM KGN for 48 hours (B, C). The media were collected and processed for Western blot analysis (A, B); total RNA was isolated for real-time reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) (C). KGN treatment alone did not stimulate the release of ITEGE while IL-1β treatment did; however, the enhanced release of ITEGE was inhibited by co-treatment with KGN and IL-1β (A, B). Increasing concentrations of KGN resulted in a proportionate decrease in ITEGE released by IL-1β-treated human chondrocytes (A). Increased release of ITEGE, ADAMTS4, and ADAMTS5 resulted from the treatment with IL-1β; however, co-incubation with KGN blocked the stimulated release of ITEGE and ADAMTS5, while ADAMTS4 did not show significant change (B). Under the same condition, KGN treatment reduced the IL-1β-induced increase of ADAMTS5 gene expression (C, n = 3; *P = 0.010, #P = 0.033).
