Figure 4.
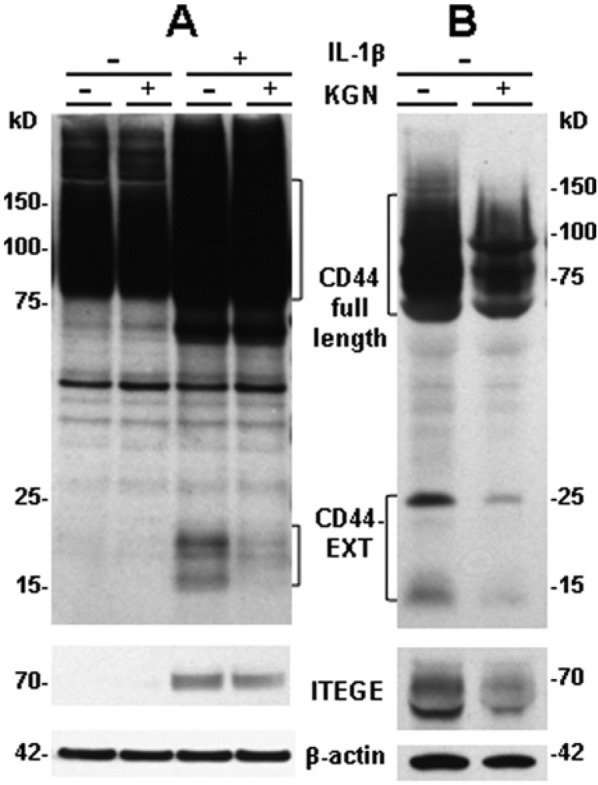
Kartogenin decreases CD44 fragmentation in bovine articular chondrocytes and in a long culture of human osteoarthritis cartilage explants. (A) Bovine articular chondrocytes were stimulated with 10 ng/mL IL-1β in the presence or absence of 10 µM kartogenin (KGN) for 48 hours. Western blot analysis of lysates revealed CD44 expression and fragmentation (CD44-EXT) detected with an anti-cytotail antibody and total β-actin. The IL-1β-stimulated fragmentation of CD44 was partially blocked when chondrocytes were co-treated with KGN but enhanced total CD44 expression persisted. Western blot analysis of media showed no G1-ITEGE unless the chondrocytes were stimulated with IL-1β, and the release of G1-ITEGE was reduced on co-treatment with KGN. Blots shown are representative of 2 independent experiments. (B) Human osteoarthritic cartilage was cultured as explants for 6 weeks in the absence or presence of 10 µM KGN. Western blot analysis of the directly extracted proteins revealed CD44 expression, total β-actin and total ITEGE. A decrease in the accumulation of G1-ITEGE in the human cartilage treated with KGN was observed accompanied by a decrease of CD44 fragmentation (CD44-EXT).
