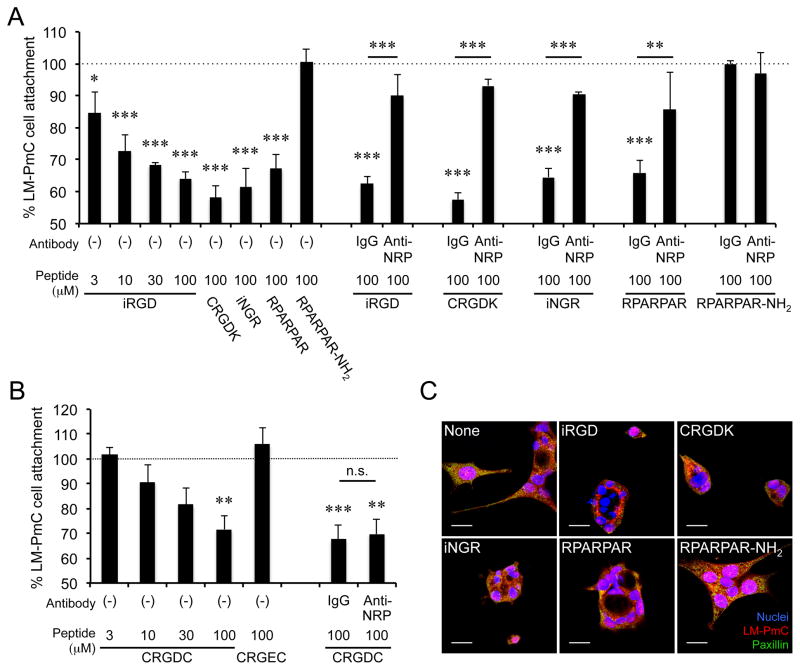
Figure 6. iRGD inhibits LM-PmC cell attachment to fibronectin in a NRP-1-dependent manner.
A and B, Cell attachment assays. The number of LM-PmC cells that attached to fibronectin-coated wells in the presence of various peptides was quantified. In A, iRGD, cleaved iRGD with an inactive RGD motif (CRGDK), non-RGD CendR peptides (iNGR: CRNGRGPDC or RPARPAR), and a RPARPAR variant that lacks affinity to NRPs (RPARPAR-NH2) were used. In B, a conventional non-CendR RGD peptide (CRGDC) and its non-integrin binding variant (CRGEC) were used. Some cells were also treated with anti-NRP-1 b1b2 or control IgG. n = 3 per experiment. Non-treated columns were considered as 100%. Error bars, mean ± SEM; statistical analyses, ANOVA; n.s., not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Statistics against non-treated columns are shown unless otherwise noted. C, Cell retraction assays. LM-PmC cells (red) cultured on fibronectin-coated coverslips were treated with 10 μM of the indicated peptides for 1 hour, fixed, and stained for phospho-paxillin (green) and nuclei (blue). Representative confocal micrographs from three independent experiments are shown. Scale bars = 20 μm.