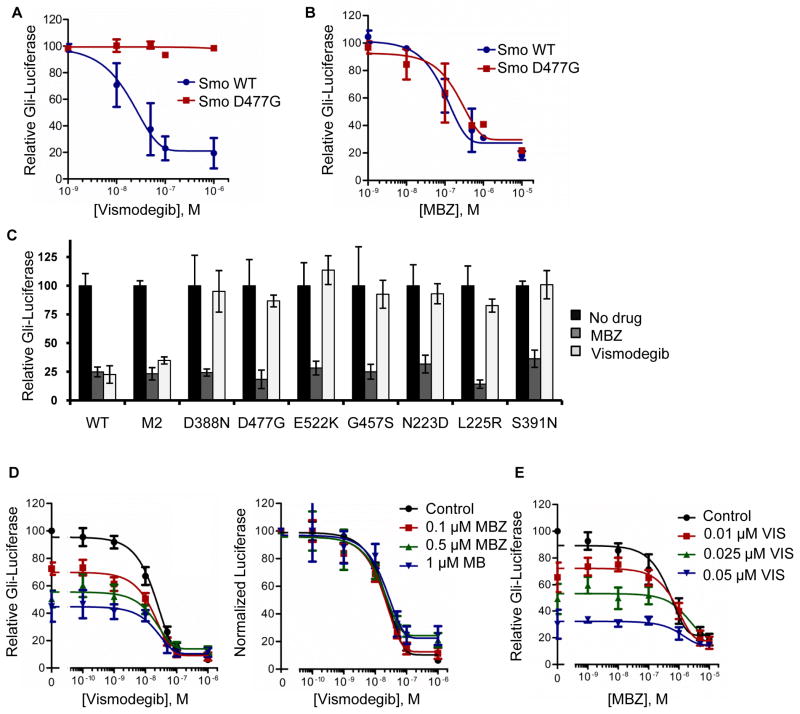
Figure 6.
Additive effects of MBZ and vismodegib against SMO signaling. Wild type Smo or the Smo D477G mutant were expressed with the Gli-luc and renilla luciferase reporters by co-transfection into Smo−/− MEFs. After 24 h, cells were treated with (A) vismodegib or (B) MBZ at the indicated concentrations, in the presence of ShhN-conditioned medium. (C) The effects of 1 μM MBZ and 0.2 μM vismodegib on Smo-dependent activation of the Gli-luc reporter were assessed against an expanded panel of Smo mutants. WT, wild type Smo. (D) The combined effects of vismodegib and MBZ on relative Gli-luc activity were tested in Shh Light2 cells under low serum conditions with supplemental ShhN-media. The relative luciferase readout was normalized to 100 for each MBZ concentration, so that the curves could be superimposed. The IC50 of vismodegib was unchanged by addition of MBZ. (E) A modification of the experiment shown in D, in which MBZ was titrated into the Shh Light2 Gli-luc assay along with fixed concentrations of vismodegib.