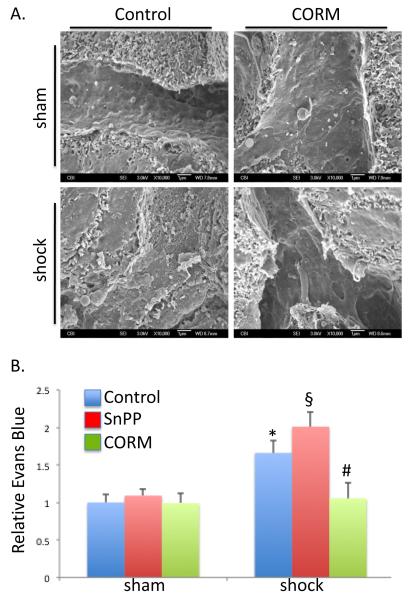
Figure 2.
Carbon monoxide-releasing molecule limited HS/R-induced hepatic microvascular injury. A. HS/R resulted in hepatic sinusoidal endothelial ultrastructural damage as demonstrated by scanning electron microscopy. Loss of normal cellular structure and hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cell fenestrations are visualized. CORM protected against these changes. B. HS/R-damaged the hepatic microvasculature as determined by Evan’s blue leak into liver tissue (*P<0.05 compared to sham, control mice). Inhibition of heme oxygenase activity with tin protoporphyrin (SnPP-IX) exacerbated microvascular injury (§P<0.05 compared to shock, control mice), whereas CORM limited this injury (#P<0.05 compared to shock, control mice).