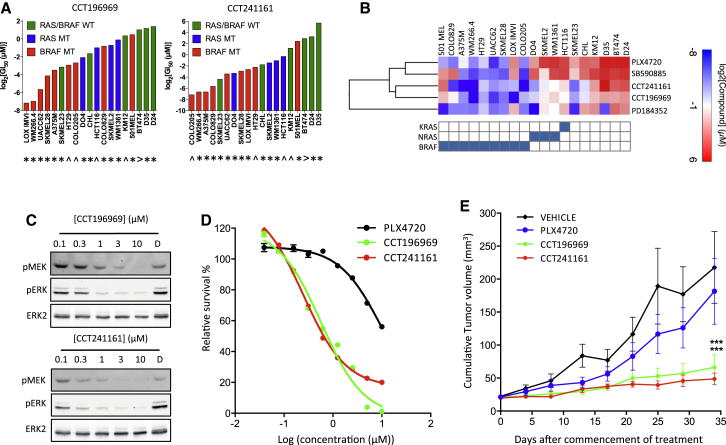
Figure 2.
CCT196969 and CCT241161 Inhibit RAS Mutant Cells
(A) Cell growth inhibition by CCT196969 or CCT241161 (expressed as log2 GI50 in micromolar) in cells carrying BRAF (red), RAS (blue), or neither (green) mutation. ∗, melanoma cell line; ˆ, colorectal carcinoma cell line; >, breast cancer cell line. WT, wild-type.
(B) Heat map showing sensitivity of cancer cell lines bearing mutations in BRAF, NRAS, or KRAS (shown in the grid below the heat map) presented as GI50 values determined after a 5-day exposure to each compound (BRAF inhibitors PLX4720 and SB590885, MEK inhibitor PD184352, and our compounds CCT241161 and CCT196969) and analysis by sulphorhodamine B staining. Values were log2-transformed, and hierarchical clustering was performed with “one minus Pearson correlation” using Gene E (www.broadinstitute.org/cancer/software/GENE-E/).
(C) Phospho-MEK (pMEK), phospho-ERK (pERK), and ERK2 in D04 cells treated for 24 hr with DMSO (D), CCT196969, or CCT241161.
(D) NRAS mutant D04 cell proliferation assay (CellTiter Glo) with PLX4720, CCT196969, or CCT241161.
(E) NRAS mutant D04 xenograft growth in nude mice treated with vehicle, PLX4720, CCT196969, or CCT241161 10 days after cell injection. ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001 (t test, two-tailed).
Bars represent SEM. See also Figure S2.