Extended Data Figure 9.
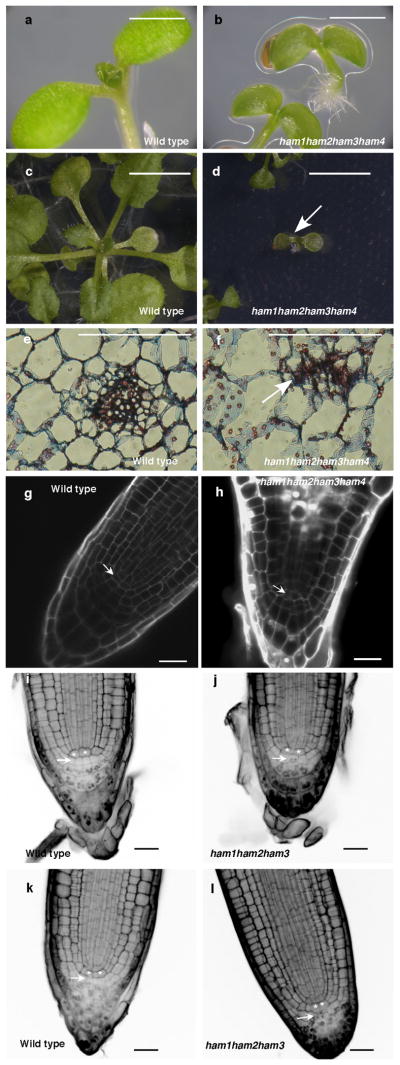
HAM family regulates various stem cell niches. (a–d) Growth arrest of ham1;2;3;4 at the seedling stage. Imaging of Ler wild type (WT) (a) and homozygous ham1;2;3;4 (b) seedlings at 7 days after germination (DAG). Imaging of WT (c) and homozygous ham1;2;3;4 (d) (arrow indicated) seedlings at 26 DAG. (e–f) Transverse section of leaves from WT (e) and ham1;2;3;4 (f) at 7 DAG. Arrow in (f) indicates undifferentiated/undetermined cell mass. (g–h) Confocal imaging of root meristem from WT (g) and ham1;2;3;4 (h) seedlings at 7 DAG. ham1;2;3;4 displayed enlarged cells with abnormal shapes at the QC (arrow indicated) and columella stem cell (CSC) positions. Cellular outlines (g–h) were visualized with PI staining (white). (i–l) mPS-PI41 stains indicate that HAM genes regulate root cell differentiation. Some CSCs (arrow indicated) undergo differentiation with starch accumulated and stained in homozygous ham1;2;3 (j, l), but none of them can be stained in L-er wild type (i, k). Asterisks mark the QC cells. Bars= 5mm (c–d), 1 mm in (a–b, e–f), 20 μm in (g–l).
