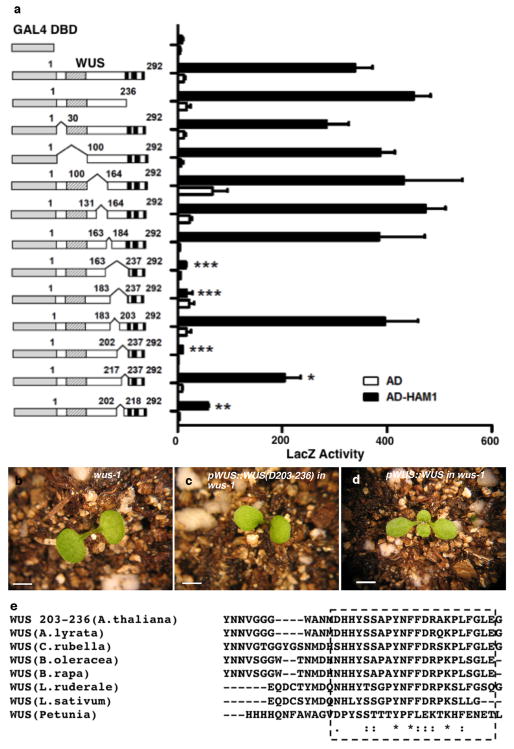
Extended Data Figure 3.
A C-terminal region of WUS is important for WUS-HAM1 interaction and is essential for WUS function in stem cell maintenance. (a) Yeast-two-hybrid assay of interactions between HAM1 and various deleted WUS derivatives. Deleting amino acids 203 to 236 (D203-236) from WUS greatly compromised the WUS-HAM1 interaction. Left panel: box diagrams of the deleted WUS derivatives; shaded boxes: the homeodomain; three black boxes: the acidic domains, the WUS box and the EAR motif, respectively. Numbers indicate amino acid residues. Error bar = mean ± sem (n=3biological replicates).*, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001(two-tailed t-test, compared to DBD-WUS full-length). (b–d) WUS function requires the same region that is important for WUS-HAM1 interaction. The terminated shoot meristem phenotype of wus-1 (b) was not complemented by WUS (D203-236) driven by WUS promoter and 3′UTR (c), and was fully complemented by the wild type WUS (d). (e) Amino acid sequence alignment of C-terminal regionsof WUS from Arabidopsis thaliana, A.lyrata, Capsella rubella, Brassica oleracea, B.rapa, Lepidium ruderale, L.sativum, and Petunia, using Clustal Omega. Asterisks: same amino acids; dots: similar amino acids. The conserved regions are boxed. Bars = 2 mm in (b–d).