Fig. 1.
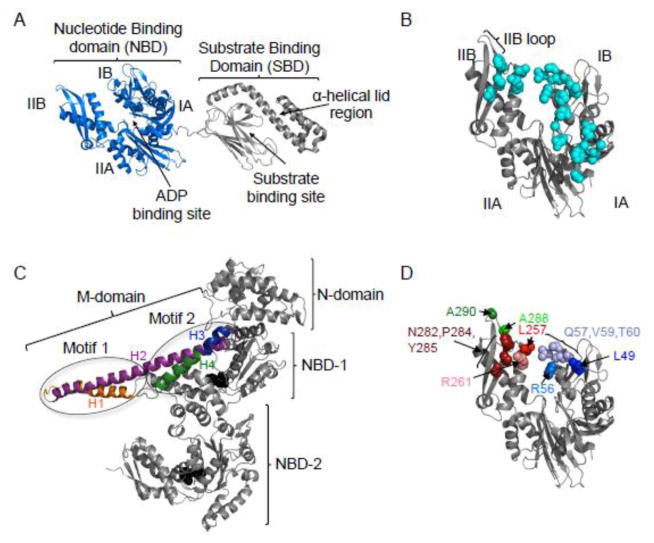
Models of the structure of E. coli DnaK and T. thermophilus ClpB. A. Solution NMR structure of DnaK in the ADP bound conformation (pdb:2KHO) 18. DnaK is comprised of an N-terminal nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) (blue), containing of four subdomains, IA, IB, IIA and IIB and a substrate-binding domain (SBD) (grey) that contains the β-sheet substrate-binding site and α-helical lid region. B. Model of the NBD of DnaK in the ADP bound conformation showing the amino acids identified as interacting with GrpE (cyan) (pdb:2KHO for structure; pdb:1DKG for GrpE binding residues) 12, 18. C. Protomer structure of T. thermophilus ClpB (PDB ID code 1qvr – chain B) 43, with the N-domain, NBD-1, NBD-2 and M-domain shown. Motif 1 and motif 2 of the M-domain identified (ovals) and the four helices of the M-domain are shown in color: H1 (orange), H2 (purple), H3 (blue) and H4 (green). ATP (black) is shown as a CPK model. D. Model of the NBD of DnaK in the ADP bound conformation showing the residues mutated in the present study (pdb:2KHO) 18. Images in A–D were made using PYMOL (www.pymol.org) 57.