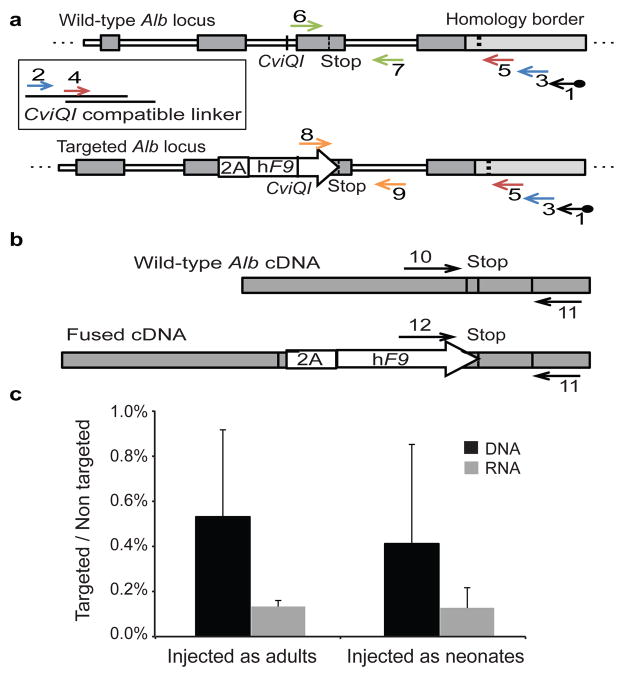
Figure 3. Rate of Alb targeting at the DNA and RNA levels.
a. Assessment of on-target integration rate begins using linear amplification (LAM) with biotinylated primer 1 (black), annealing to the genomic locus but not to the vector. Linear amplicons are then bound to streptavidinylated beads and washed to exclude episomal vectors. Subsequent second-strand DNA synthesis with random primers was followed by CviQI restriction digestion. A compatible linker is then ligated, followed by two rounds of nested PCR (primers 2–3 in blue, and then primers 4–5 in red). CviQI cleaves at the same distance from the homology border in both targeted and wild-type alleles, thus allowing for unbiased amplification. The amplicons of the 2nd nested PCR then serve as a template for qPCR assays with either primers 6–7 (green) or 8–9 (orange). b. For mRNA quantification, primers 10–11 or 11–12 were used to generate a cDNA for qPCR assays. Shape and fill code as in Fig 1. c. Black bars represent the targeting rate of Alb alleles as the ratio between the abundance of the DNA template amplified by primers 6–7 to the abundance of the DNA template amplified by primers 8–9, corrected by a factor of 0.7 to account for hepatocyte frequency. Gray bars represent the expression rate of targeted Alb alleles as the ratio between the abundance of the cDNA template amplified by primers 10–11 to the abundance of the cDNA template amplified by primers 11–12. N = 3 for each group, error bars represent standard deviation.