Table 1.
Accuracy Assessments via Linear Regression Based on Voxel Values Between Methods and Reference Standards (Truth for Simulated Brain, Prepared Concentration for Gadolinium Phantom and COSMOS for In Vivo Brain) as well as Recon Time for In Vivo Brain Imaging
| Simulated Brain | Gadolinium Phantom | In Vivo Brain | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | R2 | Slope | R2 | Slope | R2 | Time (sec) | |
| TSVD | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.99 | 0.80 | 0.45 | 1.7 |
| TKD | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.99 | 0.88 | 0.34 | 1.8 |
| iSWIM | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.99 | 0.81 | 0.48 | 14 |
| MEDI | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.59 | 1008 |
| CSC | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.87 | 0.99 | 0.79 | 0.60 | 3463(1) |
| HEIDI | 0.82 | 0.90 | 0.82 | 0.99 | 0.80 | 0.55 | 715(2) |
| TVSB | 0.83 | 0.94 | 0.87 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 0.42 | 40 |
All the calculations were performed on a PC equipped with Intel® Core i7–3770k CPU @ 3.5 GHz and 32 GB of memory, except 1 was performed on a personal laptop with Intel Core i5-M2450 CPU @ 2.5 GHz and 8 GB of memory, and 2 was performed on a PC with Intel Core i5–2320 CPU @ 3.00 GHz and 16 GB of memory.
CPU, central processing unit; COSMOS, calculation of susceptibility using multiple orientation sampling; CSC, compressed sensing compensated; GB, gigabytes; GHz, gigahertz; HEIDI, homogeneity-enabled incremental dipole inversion; iSWIM, iterative susceptibility weighted imaging and susceptibility mapping; MEDI, morphology-enabled dipole inversion; PC, personal computer; TKD, truncated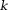 -space division; TSVD, truncated singular value decomposition; TVSB, total variation using split Bregman.
-space division; TSVD, truncated singular value decomposition; TVSB, total variation using split Bregman.
