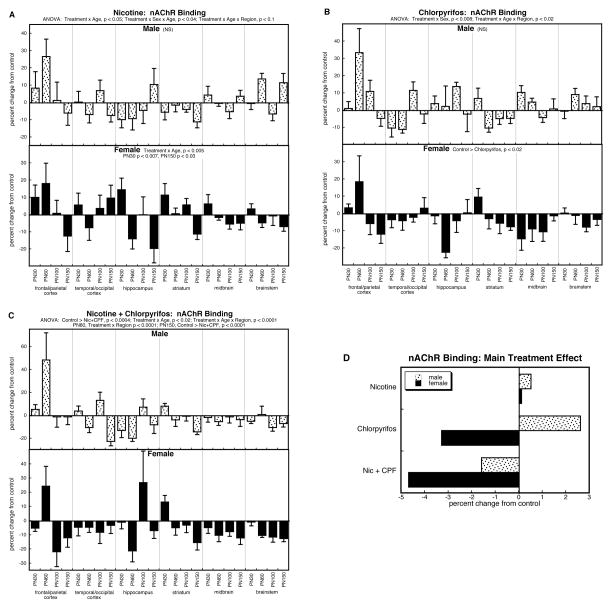
Figure 2.
Effects of nicotine (A), chlorpyrifos (B), and combined treatment (C) on nAChR binding. Data represent means and standard errors, presented as the percent change from control values; complete original data are shown in Supplement Table 3. Multivariate ANOVA for each treatment appears at the top of the panels. Lower-order tests for each sex were carried out only where there was a treatment × sex interaction (A,B) Effects on specific regions and ages are stated above or within the panels where appropriate. For (C), the interactions of treatment × age and treatment × age × region permitted further subdivision which identified significant differences for the frontal/parietal cortex on PN60 (p < 0.03), the temporal/occipital cortex on PN150 (p < 0.03), the hippocampus on PN60 (p < 0.02), the striatum on PN30 (p < 0.02) and PN150 (p < 0.006), the midbrain on PN60 (p < 0.05), and the brainstem on PN100 (p < 0.02) and PN150 (p < 0.009). Panel (D) shows the simple main treatment effects, collapsed across all the other variables.