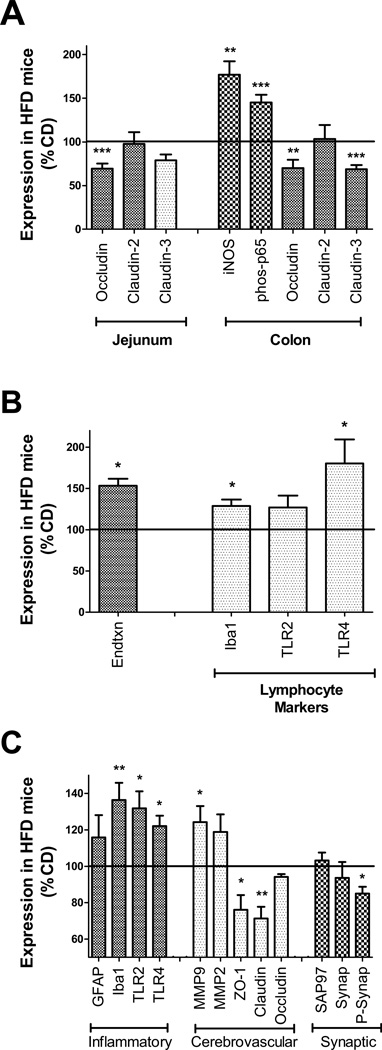
Figure 3.
Transplantation with microbiota shaped by high fat diet disrupts intestinal barrier proteins and increases systemic and brain inflammation. (A) Relative expression of tight junction proteins occludin, claudin-2, and claudin-3 in jejunum (left). Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), phosphorylated p65 (phos-p65), and tight junction proteins occludin, claudin-2, and claudin-3 in colon (right) in mice with HFD microbiota relative to CD mice. (B) Levels of plasma endotoxin, and lymphocyte expression of macrophage markers (Iba1) and TLR4, in mice with HFD microbiota as compared to CD mice. (C) Markers of inflammation, cerebrovascular integrity, and synaptic density in tissue homogenates prepared from the medial prefrontal cortex. Graphs depict increased microgliosis (Iba1) and TLR2 and TLR4 expression, increased matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) expression, and decreased expression of endothelial tight junction proteins (ZO-1 and Claudin-5) and phosphorylated synapsin-1 (P-Synap) in HFD mice. All data depict mean ± SEM expression in mice with HFD microbiota presented as % CD mice (100% line on graph), and *, **, and *** depict p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001, respectively, based on t-tests. See Supplementary Fig. S6 for representative images of all Western blot Data.