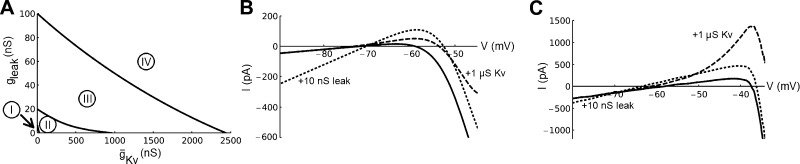
Fig. 10.
Bifurcations in the ḡKv-ḡleak plane and I–V relationships. A: different bifurcations in the ḡKv-ḡleak plane. Region I represents nonfiring, region II represents saddle-node bifurcations, region III represents loss of stability around 3 fixed points (big saddle homo-clinic bifurcations), and region IV represents Andronov-Hopf bifurcations. B: I–V curve of the neuronal model. The paramater values are those of Table 2. Dashed curve shows the effect of addition of 1 μS ḡKv and dotted curve the effect of addition of 10 nS leak conductance (reversal potential −70 mV) C: I–V curve obtained from Badel et al. (2008) based on recordings of layer 5 pyramidal neurons. Dashed curve demonstrates the effect of addition of 1 μS ḡKv and dotted curve the effect of injecting 10 nS leak conductance (reversal potential of −70 mV).