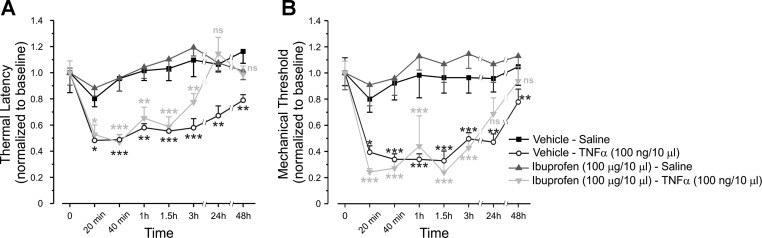
Fig. 1.
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α produces acute cyclooxygenase (COX)-2-independent hypersensitivity to noxious mechanical and thermal stimuli. Latency for paw withdrawal from hot plate (52°C), normalized to baseline (A) and mechanical threshold for paw withdrawal, normalized to baseline, measured by von Frey filaments (B), after intraplantar injection of vehicle, followed, 20 min later, by intraplantar injection of saline (Vehicle-Saline group, black squares); vehicle followed, 20 min later, by intraplantar injection of TNF-α (Vehicle-TNF-α group open circles); COX antagonist, ibuprofen, followed, 20 min later, by intraplantar injection of saline (Ibuprofen-Saline group, gray triangles); or ibuprofen followed by intraplantar injection of TNF-α (Ibuprofen-TNF-α group, light gray inverted triangles). The values are means ± SE; n = 6 for each group. Time point “0” refers to the baseline. Black asterisks, comparison between Vehicle-TNF-α group and Vehicle-Saline group; gray asterisks, comparison between Ibuprofen-TNF-α group and Ibuprofen-Saline group. Nonsignificant (ns), P > 0.05; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05; two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test.