Figure 3.
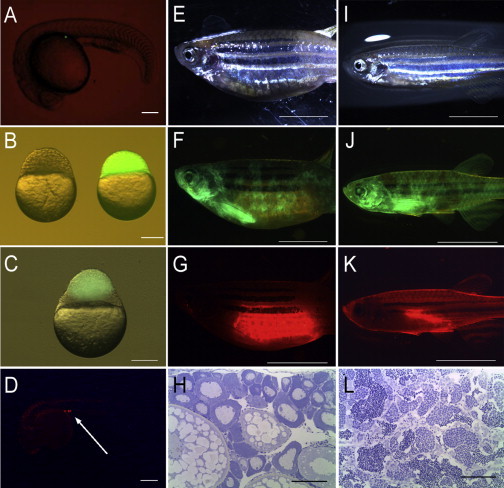
Germline Chimeras Produced by Cell Transplantation, SPT and BdT, in Zebrafish
(A) A single PGC with GFP fluorescence located at the gonadal ridge in a SPT chimera at the 25 somite stage.
(B) The recipient of golden zebrafish (left) and the donor of Tg(vasa:DsRed2-vasa);Tg(bactin:EGFP) double transgenic embryos (right) used for the generation of BdT chimeras.
(C) A donor blastoderm with GFP fluorescence attached to the host blastoderm a few hours after transplantation.
(D) Donor-derived PGCs with RFP fluorescence were at the gonadal ridge at the prim-5 stage in a BdT chimera (arrow).
(E–L) Representative female (E–G) and male (I–K) BdT chimeras were imaged under bright field (E and I), GFP fluorescence (F and J), and RFP fluorescence (G and K). Histological analysis of selected gonads (n = 5) from germline chimeras confirmed the presence of an ovary (H) or a testis (L).
Scale bars represent 20 μm (A–D), 500 μm (E–G and I–K), and 100 μm (H and L). See also Table S1 for the survival rates following these manipulations and Movies S1 and S2 for BdT.
