Figure 5.
Single-Cell Electrophysiology of SHOX2-EBs Demonstrate SAN Pacemaker Cell-like Electrophysiology
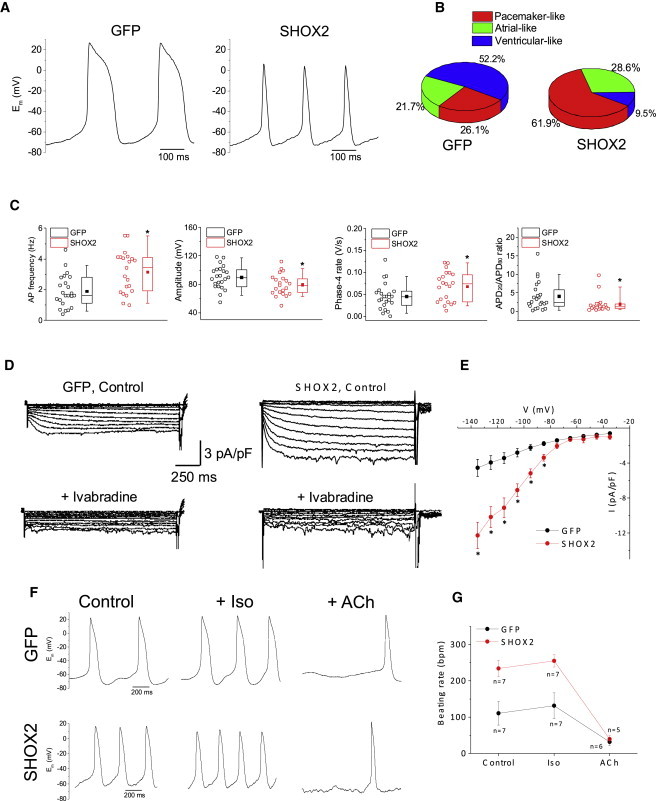
(A) Representative raw traces of APs recorded from spontaneously-beating single cells from GFP-EBs (left) or SHOX2-EBs (right).
(B) Percentage of cells with pacemaker-like, atrial-like, or ventricular-like APs in GFP (n = 23) and SHOX2 (n = 21) groups.
(C) Comparison of AP parameters (from left to right): spontaneous beating rate, amplitude of the AP upstroke, spontaneous phase 4 diastolic depolarization rate, and ratio of AP duration at 20% repolarization (APD20) to 80% repolarization (APD80). ∗p < 0.05.
(D) Representative HCN ionic currents (If) recorded from a GFP-EB cell (left) and a SHOX2-EB cell (right). Lower panels show the inhibition of time-dependent currents upon addition of 10 μM ivabradine in the bath solution. HCN currents were recorded in normal Tyrode’s solution containing 1 mM BaCl2 in order to block contaminating inward rectifier K+ currents. The If currents were elicited with a family of voltage steps from −135 mV to +35 mV for 1.5 s with 10 mV increment from a holding potential of −35 mV.
(E) Current density-voltage relationships of GFP (black, n = 4) and SHOX2 (red, n = 5) groups. ∗p < 0.05.
(F) Representative APs of a GFP cell (top row) and a SHOX2 cell (bottom row) before (left) and after treatment with isoproterenol (Iso, 1 μM, middle) or acetylcholine (ACh, 50 nM, right).
(G) Summary of beating rate responses before and after treatment with isoproterenol or acetylcholine. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. All experiments were performed on three independent biological replicates.
