Figure 4.
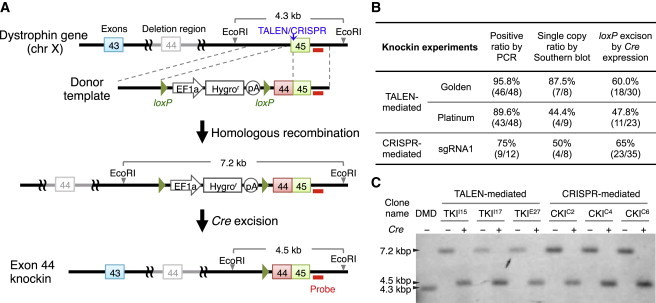
Correction of the Full-Length Dystrophin Protein by Exon 44 Knockin
(A) Schematic overview depicting the exon 44 knockin strategy. Top line: structure of the dystrophin gene with the exon 44 deletion. The vertical blue arrow indicates the TALEN/CRISPR cut site and the red bar indicates the intron 45 probe used for Southern blot analysis. Note that we introduced silent mutations at the nuclease-targeting site within exon 45 of the donor template.
(B) Summary of the exon 44 knockin experiments. The picked clones were first screened by genomic PCR for targeted knockin of the donor template and then by Southern blotting with EcoRI digestion and the intron 45 probe to confirm no additional integration. Successfully targeted clones were further treated with Cre to remove the drug selection cassette flanked by the loxP elements.
(C) Southern blot of the knockin clones (clone names: TKII15, TKII17, and TKIE27 for TALEN-mediated knockin clones; CKIC2, CKIC4, and CKIC6 for CRISPR-mediated knockin clones) showing successful targeting at the designated site. Subsequent Cre treatment excised the loxP-flanked drug selection cassette. The probe in intron 45 was used to detect EcoRI-digested genomic DNA fragments.
See also Figures S3B and S3C.
