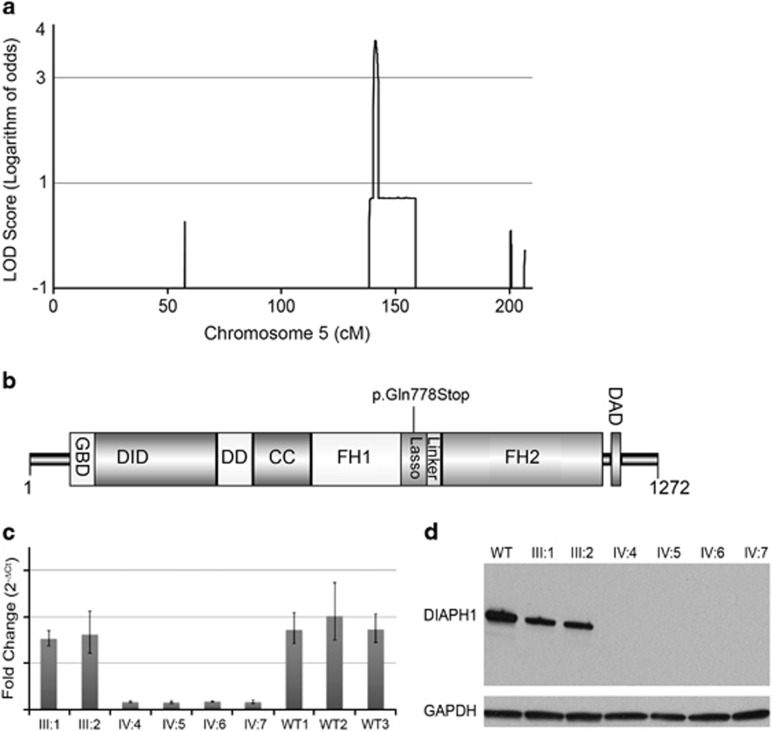
Figure 2.
Identification of a nonsense homozygous sequence variant in the DIAPH1 gene in a family with MCP. (a) Panel shows the results of the parametric linkage analysis for chromosome 5q, expressed as LOD scores. The maximum theoretical LOD score for this family is 3.7 using the genotyping data from IMv1 Duo Bead array chips. The analysis is modeled under the recessive mode of inheritance, penetrance of 99%, a phenocopy rate of 0.01, and a disease allele frequency of 0.0001. (b) Domain organization of mDia1. Abbreviations: GBD, GTPase binding region; DID, diaphanous inhibitory domain; DD, dimerization domain; CC, coiled coil; FH1, formin homology 1 domain; FH2, formin homology 2 domain; DAD, diaphanous autoinhibitory domain. Nonsense sequence variant p.Gln778* results in a 86.2 kDa truncated protein. (c) mRNA levels of DIAPH1 gene in EBV transformed LCLs from homozygous patients (IV:4, IV:5, IV:6, IV:7), and heterozygous parents (III:1 and III:2) were analyzed using RT-PCR. Three individuals of the same ethnicity and without a sequence variant are used as control (WT). (d) Protein blot for mDia1. Lane 1 represents the control subject, lanes 2 and 3 represent the unaffected parents who carry the heterozygous p.Gln778* alteration (III:1 and III:2). Lanes 4, 5, 6, and 7 represent affected individuals with homozygous p.Gln778* alteration (IV:4, IV:5, IV:6, IV:7). The band indicates a molecular weight of ∼140 kDa. GAPDH is used as control (lower band).