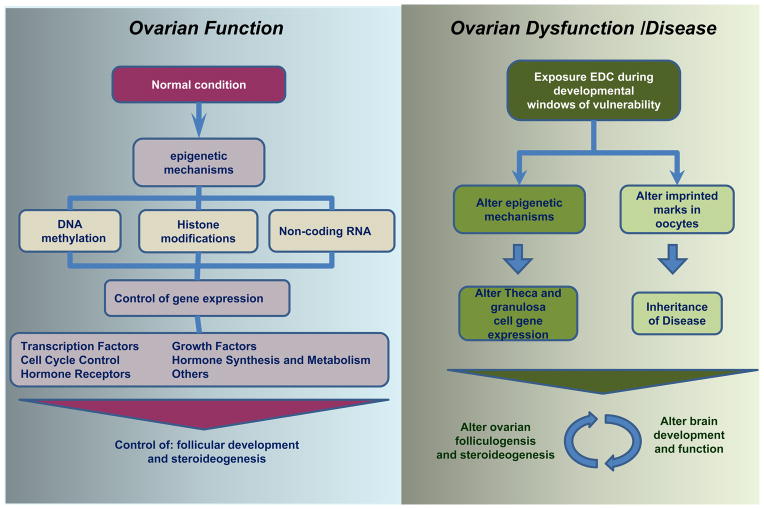
Figure 2. Developmental EDC exposure and potential epigenetic mechanisms in altered brain and ovarian function.
The normal ovarian development and function are strictly regulated by precise epigenetic mechanisms (DNA methylation, histone modifications, and miRNA) that coordinate the spatio-temporal expression of key genes. These genes are transcription factors, cell cycle proteins, growth factors, hormone synthesis enzymes and receptors, which participate in different stages of development of the follicles. Exposure to environmental estrogens alters these mechanisms of control, affecting gene expression in the ovary and leading to dysfunction and disease (See section 3).