Fig. 2.
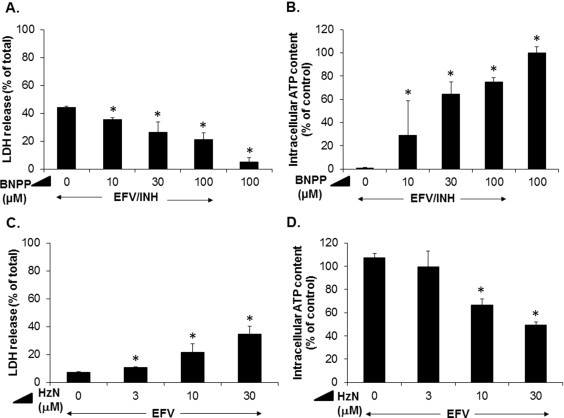
Role of hydrazine (HzN) in EFV/INH-induced hepatocellular injury. (A and B) Concentration-dependent effects of bis-p-nitrophenyl phosphate (BNPP, an inhibitor of acylamidase-mediated hydrolysis of INH to HzN), on cell injury and intracellular ATP concentrations caused by exposure of cultured mouse hepatocytes to a combination of EFV (30 μM) and INH (1000 μM) for 24 h. Data are mean ± SD of three independent hepatocyte preparations using quadruplicate wells. *P < 0.05 versus no addition of BNPP. (C and D) Concentration-dependent effects of HzN in combination with a fixed concentration (30 μM) of EFV on LDH release and intracellular ATP content after 24 h. Data are mean ± SD of three independent hepatocyte preparations using quadruplicate wells. *P < 0.05 versus EFV alone.
