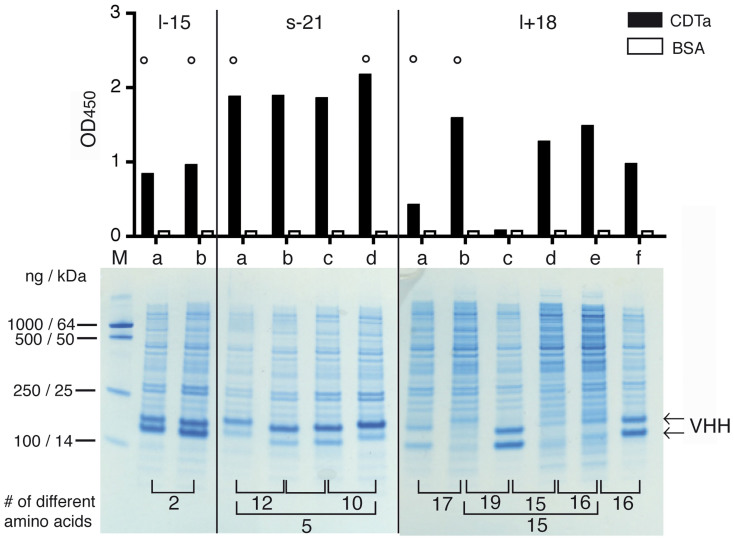
Figure 2. Production of monovalent nanobodies in the E. coli periplasm and verification of binding specificities.
E. coli HB2151 cells were transformed with individual VHH-encoding pHEN2 vectors and protein expression was induced with IPTG for 3 h. Periplasmic lysates were prepared by osmotic shock, clarified by centrifugation, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining (bottom). Binding specificity was analyzed by ELISA using CDTa or BSA as a control protein (top). Representative results are shown for three families of CDTa-specific nanobodies. Results for CDTb-specific families are shown in Supplementary Fig. S2. Family names indicate the presence of a long or short hinge, the absence or presence of an additional cysteine pair in CDRs 2 and 3, and the number of amino acid residues in the CDR3 (see Table I). Family members with distinct amino acid sequences were designated a, b, c, d etc. in order of decreasing number of isolates. Numbers on the bottom indicate the number of different amino acids between two family members. Nanobodies marked by a circle were selected for subcloning into a eucaryotic expression vector.