Abstract
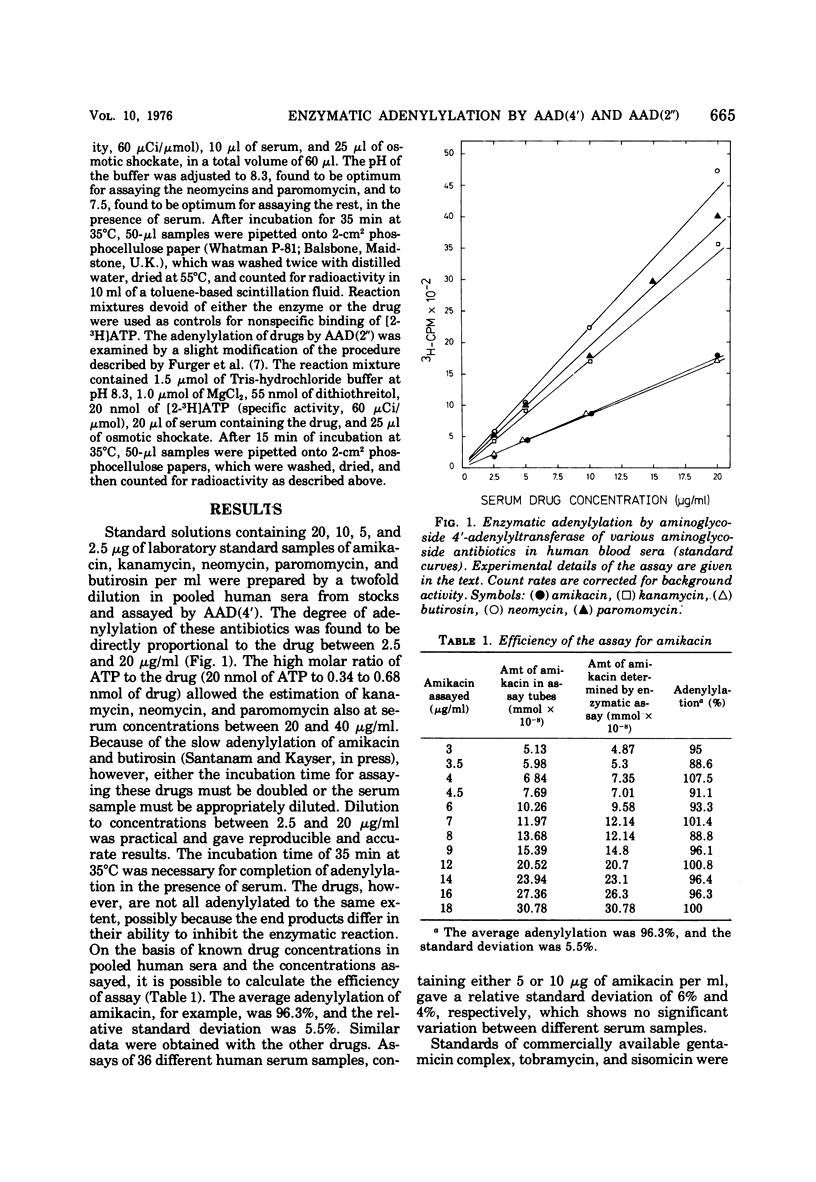
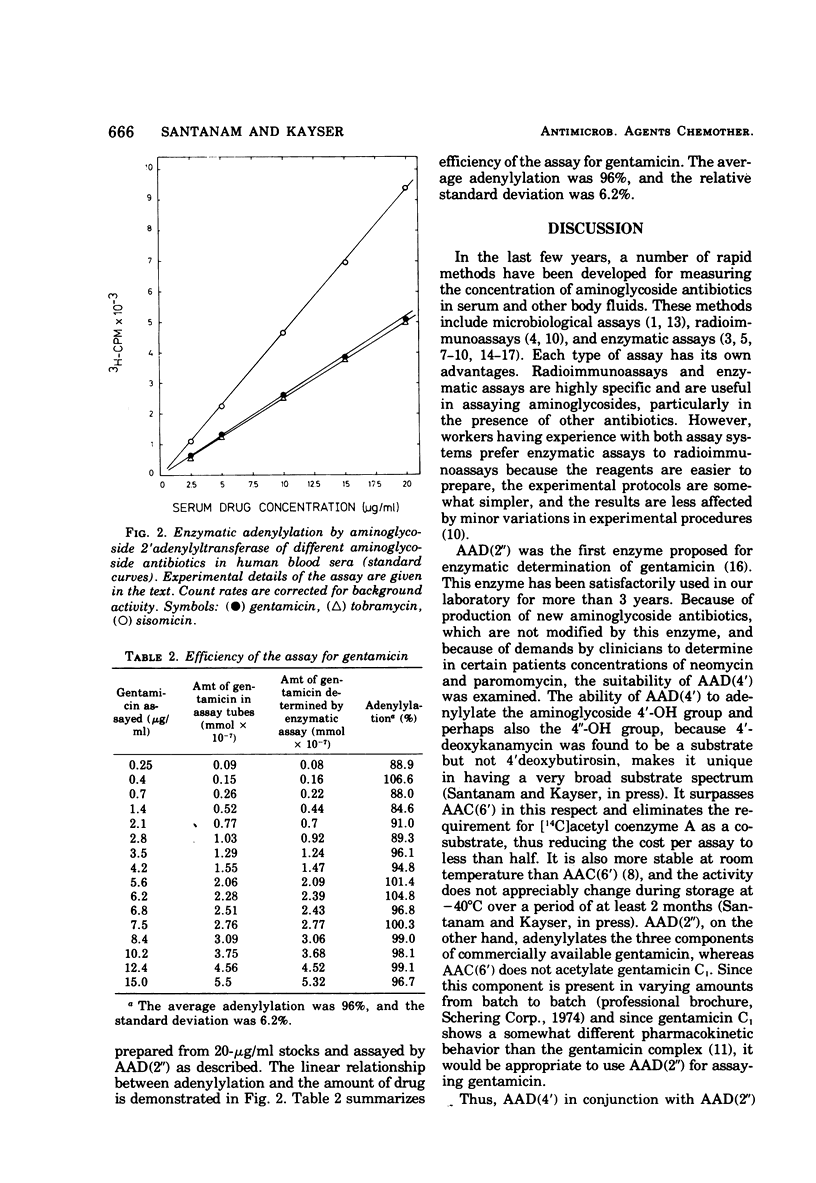
A fast and accurate enzymatic estimation of the concentration of aminoglycoside antiobiotics in serum is given by aminoglycoside 4′-adenylyltransferase (synonym: tobramycin adenylyltransferase), a new enzyme recently found in tobramycin-resistant staphylococci (P. Santanam and F. H. Kayser, J. Infect. Dis. [Suppl.], in press). This enzyme is useful in assaying the kanamycins, the butirosins, amikacin, ribostamycin and, if required, the neomycins, tobramycin, and paromomycin. In combination with the assay using aminoglycoside 2′′-adenylyltransferase (synonym: gentamicin adenylyltransferase) to determine the level of gentamicin, sisomicin, and tobramycin, a convenient method to estimate a wide range of aminoglycoside antibiotics in patients' sera is described.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Yamada T., Davies J. Enzymatic Adenylylation of Streptomycin and Spectinomycin by R-Factor-Resistant Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1970 Jan;1(1):109–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.1.109-119.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughall J. M., Reeves D. S. Properties of the gentamicin acetyltransferase enzyme and application to the assay of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Aug;8(2):222–223. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.2.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughton A., Strong J. E. Radioimmunoassay of antibiotics and chemotherapeutic agents. Clin Chem. 1976 Jun;22(6):726–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daigneault R., Gagné M., Brazeau M. A comparison of two methods of gentamicin assay: an enzymatic procedure and an agar diffusion technique. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):642–645. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furger F., Russi A., Kayser F. H. Schnellmethoden zur quantitativen Bestimmung von Aminoglykosid-Antibiotika. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1973 May 26;103(21):779–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. J., Davies J. Enzymatic acetylation as a means of determining serum aminoglycoside concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):497–499. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Sanford J. P. Enzymatic assay for gentamicin and related aminoglycoside antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):519–527. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshew B. H., Holmes R. K., Baxter C. R. Comparison of a radioimmunoassay with an enzymatic assay for gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):107–109. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosegaard A., Welling P. G., Madsen P. O. Gentamicin and gentamicin C1 in the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections: comparative study of efficacy, tolerance, and pharmacokinetics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):328–332. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noone P., Pattison J. R., Samson D. Simple, rapid method for assay of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Lancet. 1971 Jul 3;2(7714):16–19. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Smith D. H. Gentamicin:adenine mononucleotide transferase: partial purification, characterization, and use in the clinical quantitation of gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1974 Apr;129(4):391–401. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Van Otto B., Smith A. L. A rapid chemical assay for gentamicin. N Engl J Med. 1972 Mar 16;286(11):583–586. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197203162861106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Improved acetylating radioenzymatic assay of amikacin, tobramycin, and sisomicin in serum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):374–376. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. W., Langer J. S., Northrop D. B. A spectrophotometric assay for gentamicin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1975 Dec;28(12):982–987. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.28.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


