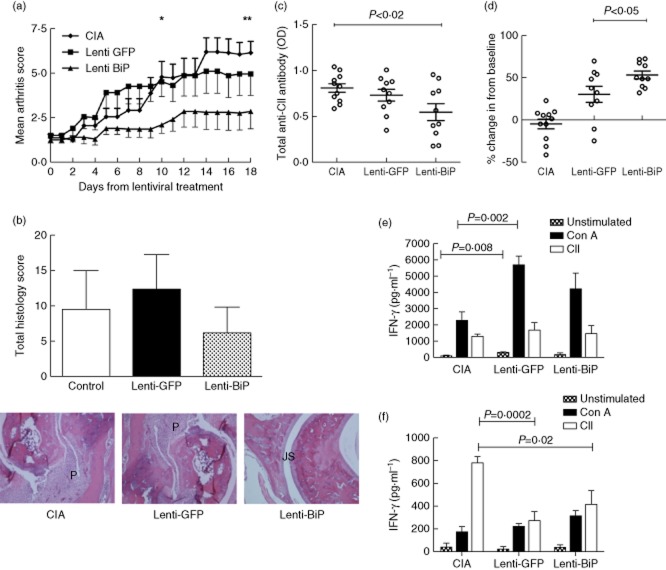
Figure 2.
Low-dose lentiviral vector containing the murine binding immunoglobulin protein (Lenti-mBiP) treatment improves histological and serological parameters of collagen-induced arthritis. Dilute brown non-Agouti/1 (DBA/1) mice (n = 10 or 11/group) were either untreated or treated with 1 × 107 infectious viral vector particles of either Lenti-green fluorescent protein (GFP) or Lenti-mBiP administered intraperitoneally at disease onset. (a) Clinical arthritis scores were assessed regularly up to day 18 post-treatment. Data represents the mean and standard error of the mean (*P < 0·03 Lenti-GFP versus Lenti-BiP; **P < 0·01 CIA versus Lenti-BiP; significance was determined using Kruskal–Wallis one-way analysis of variance) (b) Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining (magnification ×100) of representative animals with median pathology in the hind paws from the different treatment groups. P = pannus, JS = normal joint space. A histogram shows the mean and standard deviation of the histological scores for each group of five animals. (c) At termination the serum level of total anti collagen type II (CII) immunoglobulin (Ig)G antibodies was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and (d) the percentage increase in anti-BiP IgG levels from the individual baseline level at the start of the study was recorded. Mixed lymph node and splenocytes (2·5 × 106) were cultured and restimulated with 40 μg/ml CII or 2 μg/ml concanavalin A (ConA). Interferon (IFN)-γ (e) and interleukin (IL)-10 (f) concentrations in culture supernatants were determined at 72 h by carboxyethyl lysine ELISA (CelELISA) (n = 5/group). Statistical significance was analysed using GraphPad software and significance was determined using unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. Significance was taken as <0·05 and the values are as shown.