Figure 3.
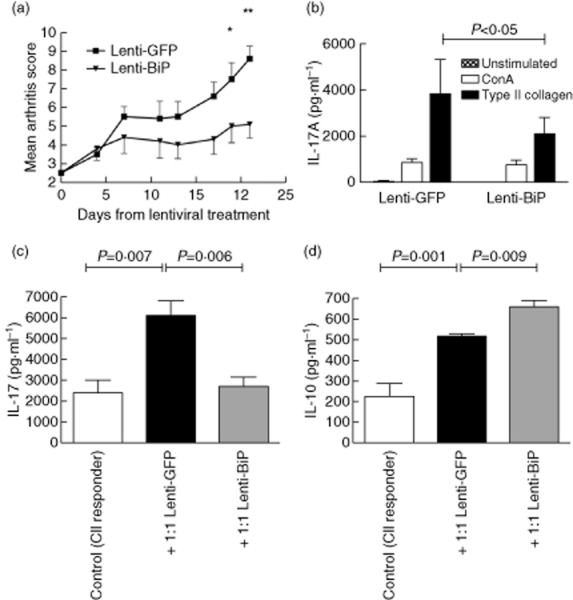
High-dose lentiviral vector containing the murine binding immunoglobulin protein (Lenti-mBiP) treatment ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) and suppresses collagen-specific interleukin (IL)-17 responses: dilute brown non-Agouti/1 (DBA/1) mice (n = 10/group) were treated with 2·5 × 107 infectious viral particles of either Lenti-green fluorescent protein (GFP) (Lenti-GFP) or Lenti-mBiP administered intraperitoneally at onset of mild arthritis (clinical score 2). (a) Clinical arthritis scores were assessed regularly for a further 21 days after treatment. The mean ± standard error of the mean is shown. *P < 0·05 Lenti-GFP versus Lenti-BiP; **P < 0·005 Lenti-GFP versus Lenti-BiP (significance was determined using Kruskal–Wallis one-way analysis of variance). (b) Spleens and lymph nodes were dissected at termination and 2·5 × 106 cells were either unstimulated or stimulated with concanavalin A (ConA) (2 μg/ml) or type II collagen (CII)(40 μg/ml) as shown. Single-cell cultures of mixed splenocytes and lymph node cells from either control collagen-induced arthritis (CIA), Lenti-GFP or Lenti-mBiP individual mice were used in co-culture with CII primed cells (1·25·106). Cells were stimulated for 72 h with CII (40 μg/ml). (c) IL-17A and (d) IL-10 secretion was measured by carboxyethyl lysine enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (CelELISA). The mean ± standard error of the mean is shown. (n = 4/group). Statistical significance was analysed using GraphPad software and significance was determined using the unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. Significance was taken as <0·05 and the values are as shown.
