Figure 1.
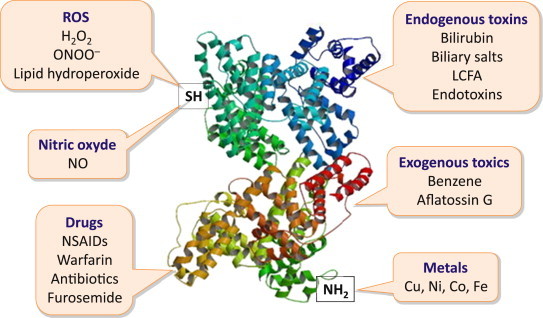
Albumin possesses functional domains with important properties, such as the free cysteine residue (SH) in position 34, which exerts potent anti-oxydant and scavenging activities, the aminoterminal (NH2) that binds to and removes highly toxic reactive metal species, and other domains that bind a variety of endogenous and exogenous substances including endotoxins and various drugs (ROS: reactive oxygen species; LCFA: long-chain fatty acids; NSAIDs: non-steroideal anti-inflammatory drugs).
