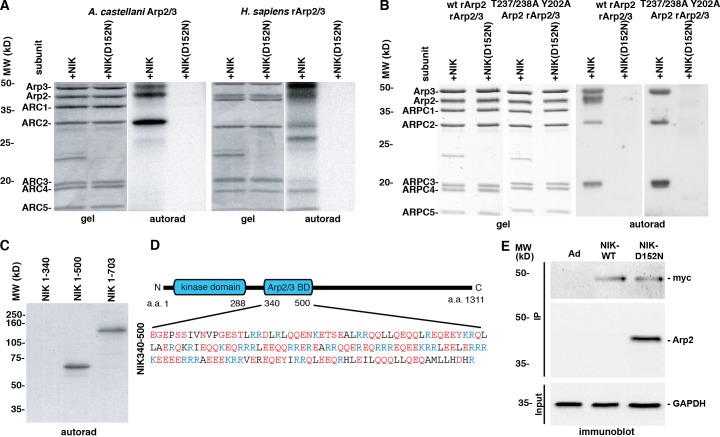
Figure 3.
NIK phosphorylates and binds the Arp2/3 complex. (A) In vitro, WT NIK but not kinase-inactive NIK-D152N phosphorylates Arp3, Arp2, and ARPC1 subunits of the Arp2/3 complex purified from A. castellanii and from baculovirus expression of human recombinant Arp2/3 complex (rArp2/3). (B) NIK phosphorylation of Arp2 but not Arp3 and ARPC3 subunits is not seen with rArp2/3 complex containing a mutant Arp2-T237/238A-Y202A. (C) Arp2/3 complex coupled to CH-Sepharose and incubated with recombinant NIK 1–340, NIK 1–500, and NIK 1–703 shows that the NIK region of amino acids 340–500 binds the Arp2/3 complex. (D) Schematic of NIK showing the kinase domain and proposed Arp2/3 complex binding domain, which contains abundant acidic (red) and basic (blue) residues. (E) Arp2 coprecipitates in Myc immune complexes of MTLn3 cells transiently expressing Myc-tagged NIK-D152N by not with Myc-tagged WT NIK or empty adenovirus (Ad).