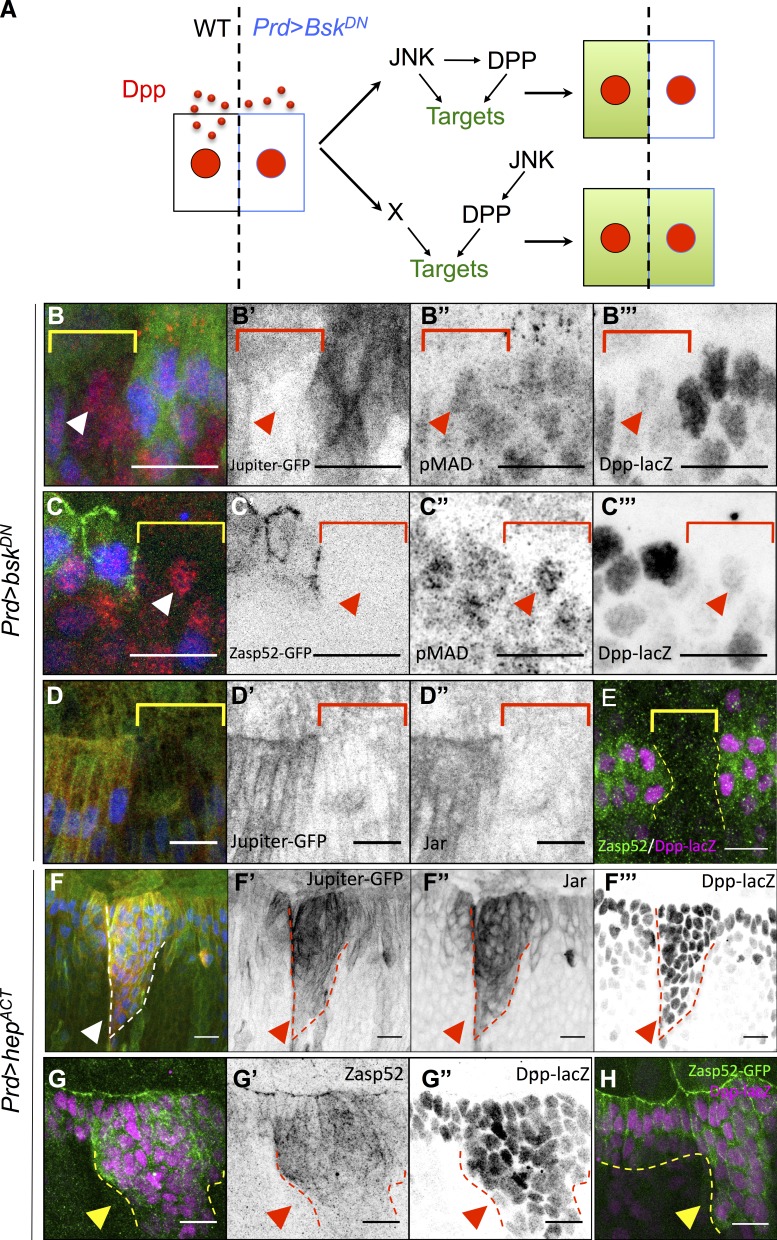
Figure 3.
JNK and DPP form a coherent FFL that regulates cell differentiation. (A) Experimental design. The wild-type (WT) cell (black rectangle) secretes DPP (red dots) that induces its pathway in all cells (red nuclei). The absence of target (green) in the Prd>BskDN cell abutting the wild-type cell indicates the presence of a JNK/DPP FFL. (B–C‴) Prd-Gal4, UAS-bskDN, Dpp-lacZ embryos marked for Jupiter::GFP (green in B; gray in B′) or Zasp52::GFP (green in C; gray in C′), phospho-Mad (red in B and C; gray in B″ and C″), and lacZ (blue in B and C; gray in B‴ and C‴). The brackets indicate the BskDN domain, where DPP-lacZ (blue) is off. Anti–phospho-Mad (red) indicates that all cells receive DPP. Jupiter (B) and Zasp52 (C) in green are excluded from the BskDN territory, even though DPP signaling is active (arrowheads), indicating that JNK acts also in parallel of DPP. (D–D″) Prd-Gal4, UAS-bskDN, Dpp-lacZ embryos marked for Jupiter::GFP (green in D; gray in D′) Jar (red in D; gray in D″) and lacZ (blue in D; gray in D‴). (E) Prd-Gal4, UAS-bskDN, Dpp-lacZ embryos marked for Zasp52::GFP and lacZ. All the markers are lost in the entire BskDN territory (brackets in B–D or dotted lines in E). (F) Prd-Gal4, UAS-hepACT, Dpp-lacZ, Jupiter::GFP embryos marked for Jupiter::GFP (green in F; gray in F′), Jar (red in F; gray in F″), and lacZ (blue in F; gray in F‴). (G–H) Prd-Gal4, UAS-hepACT, Dpp-lacZ embryos marked for lacZ (magenta in G and H; gray in G″) and Zasp52 (green in G; gray in G′) or Zasp52::GFP (green in H). Ectopic JNK activity (dotted lines) induces Jar, Jupiter, and Zasp52 accumulation (arrowheads). Bars, 10 µm.