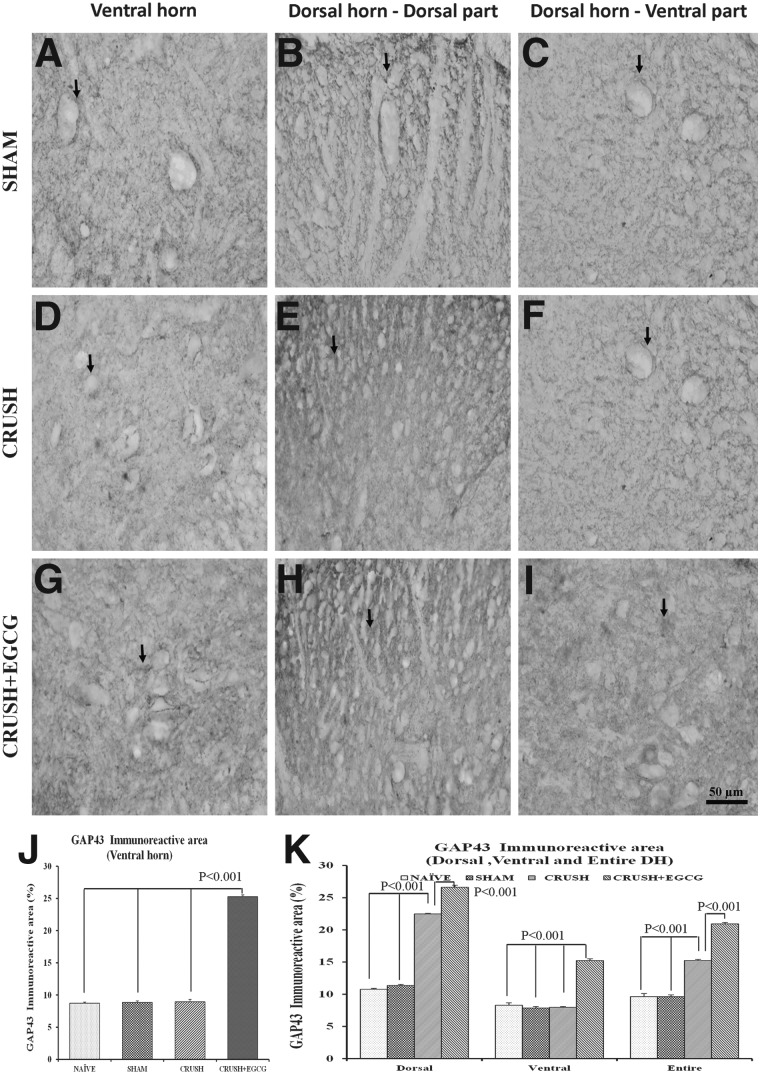
FIG. 10.
(A–I) GAP-43-stained photomicrographs of the ventral horn (left panel: A, D, G), dorsal part of the dorsal horn (middle panel: B, E, H), and ventral part of the dorsal horn (right panel: C, F, I) from SHAM, CRUSH, and CRUSH+EGCG groups of rats at 1 week postsurgery. Arrows indicate the GAP-43 staining. Note the significant increase in GAP-43 immunoreactivity in the CRUSH+EGCG group in the dorsal and ventral horns. Scale bar=50 μm, applicable to all photomicrographs. (J and K) Bar chart illustrating GAP-43 immunoreactive area (%) in the ventral horn (J) and dorsal horn (K), as measured by Scion Image analysis software (National Institutes of Health) in different groups. Data represent mean±SEM (n=6 in all groups; ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post-test). EGCG, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate; GAP-43, growth-associated protein 43; DH, dorsal horn.