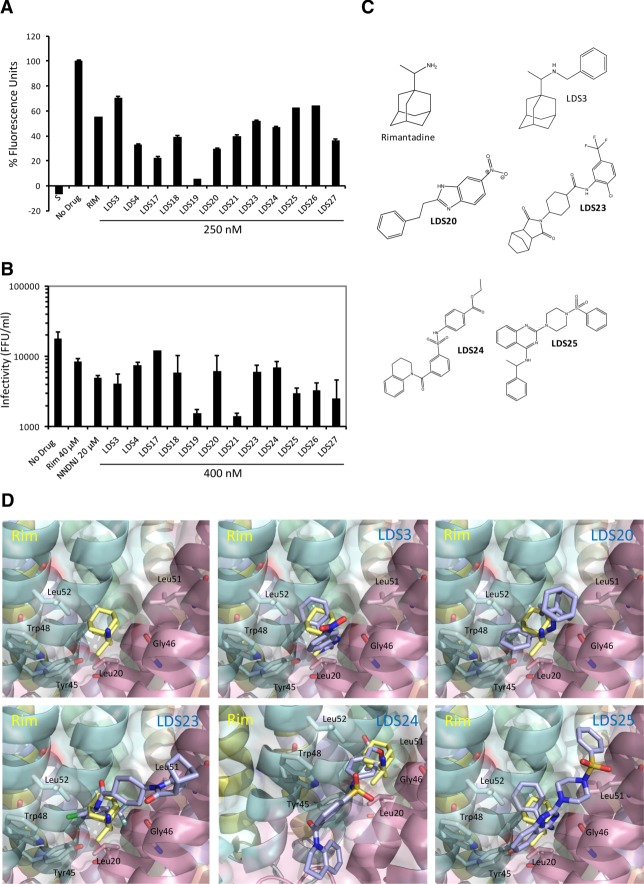
Figure 4.
Selection of novel, structurally diverse p7 inhibitors. In silico screening using p7 channel models as a template derived a range of Lipinski-compliant potential inhibitors of the p7 channel complex and the top 30 were selected for testing as proof-of-principle. (A) Liposome dye release assay showing endpoint values compounds with activity against wild-type p7 at 250 nM that were subsequently selected for cell culture studies. Results are the average of two separate experiments with each condition in duplicate and are expressed as a percentage of the untreated protein value following baseline subtraction (liposomes alone). S, solvent control. p7 treated with one rimantadine IC50 (40 μM) is included as comparison, novel compounds tested at 250 nM. (B) Inhibition of infectious virus release from Huh7 cells transfected with J4/JFH-1 RNA using novel compounds (400 nM). Selected compounds show minimal effect on intracellular infectivity, replicon replication and have no toxic effects (see Supporting Fig. 5 and Table 2). Chart shows the average released titers from duplicate wells originating from at least two separate experiments, error bars represent standard error between experiments. Rimantadine and the alkylated imino-sugar NN-DNJ at ∼IC50 are shown for comparison (40 and 20 μM, respectively). (C) Structures of selected initial hit compounds. (D) Predicted docking poses of rimantadine novel compounds at the allosteric binding site (calculated in Glide, Schrodinger). Key interacting residues are highlighted.