Fig. 1.
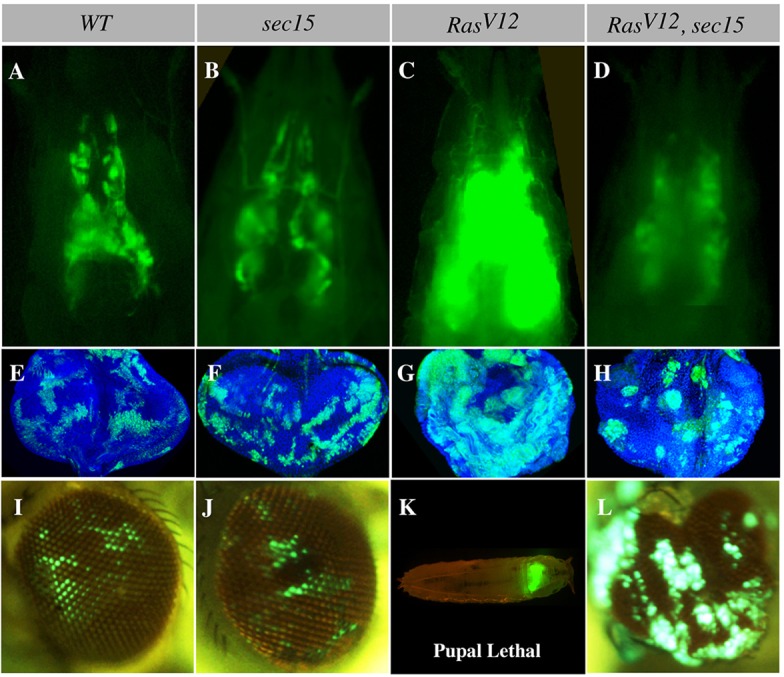
RasV12 and sec15 synthetic lethal interaction. (A-D) Intact third instar larval cephalic regions showing wild-type (WT), sec15, RasV12 and RasV12, sec15 double mutant eye-antenna disc clones. Wild-type (A) and sec15 (B) clones are comparable in size, whereas RasV12 clones (C) overgrow to develop tumors. The sec15 mutation suppresses RasV12 tumor growth (D). (E-H) Similarly aged eye discs bearing wild-type, sec15, RasV12 and RasV12, sec15 double mutant clones. Wild-type (E) and sec15 (F) clones show a comparable sparse pattern, whereas RasV12 clones (G) overgrow to form large contiguous tumors. However, RasV12, sec15 double mutant clones are sparse and smaller (H). (I-L) Adult eyes showing lethality and contribution of larval clones to the eye field. Wild-type (I) and sec15 (J) clones similarly persist into the adult eye and do not cause animal lethality. RasV12 clones (K) are pupal lethal but animal lethality is suppressed in animals bearing RasV12, sec15 double mutant clones, and cells of this genotype now contribute to the adult eye (L).
