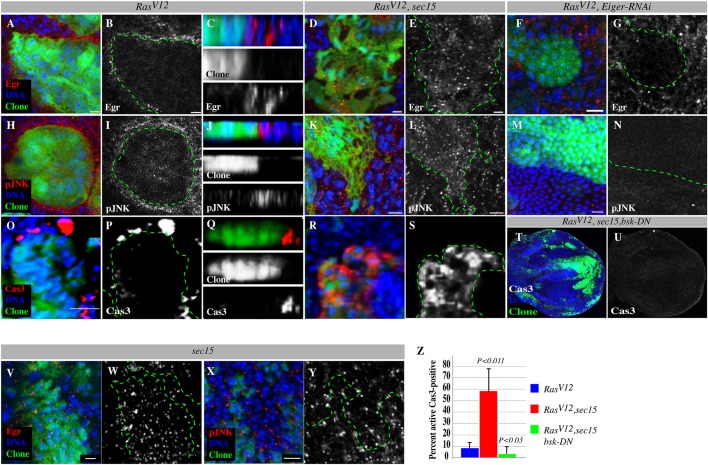
Fig. 5.
Sec15-dependent Eiger exocytosis suppresses JNK-induced cell death in RasV12 cells but promotes JNK activation in the surrounding wild-type cells. (A-Y) Comparable z-sections showing RasV12 or RasV12, sec15 double mutant clones or RasV12, eiger-RNAi clones (green) stained with anti-Eiger (red) or anti-phospho-JNK (pJNK, red) to detect JNK signaling activity or anti-active caspase 3 to detect apoptotic cells, and with DAPI (blue) to mark DNA. Gray panels show Eiger, phospho-JNK or caspase 3 channels alone. The dotted green lines denote clone boundaries. C,J and Q are z-section views. Eiger is concentrated at the boundary of RasV12 clones (A-C) but not at the boundary of RasV12, sec15 (D,E) or RasV12, eiger-RNAi (F,G) clones. Eiger is moderately retained in sec15 clones (V,W) but is present at higher levels in RasV12, sec15 double mutant clones (D,E). Wild-type cells surrounding RasV12 clones (H-J), but not wild-type cells surrounding RasV12, sec15 (K,L) or RasV12, eiger-RNAi (M,N) clones show elevated phospho-JNK levels. RasV12, sec15 double mutant clones show elevated phospho-JNK levels (K,L). Correspondingly, cell death can be detected in wild-type cells surrounding RasV12 clones (O-Q) but not in wild-type cells surrounding RasV12, sec15 double mutant clones. Instead, cell death is concentrated inside the double mutant clones (R,S). (T,U) Confocal projection showing discs containing RasV12, sec15, bsk-DN triple mutant clones stained with DAPI to mark nuclei and stained for active caspase-3 to detect apoptotic cells. The caspase channel alone is shown in U. (X,Y) sec15 mutant cells stained with DAPI and anti-phospho-JNK. (Z) Quantification of caspase-positive cells in RasV12 single or RasV12, sec15 double or RasV12, sec15, bsk-DN triple mutant clones. Error bars denote standard deviations from the mean for each genotype analyzed. P values are derived from a two-tailed distribution with two-sample equal variance t-test. Scale bars: 5 μm.