Figure 3. ARC knockdown leads to dose-dependent rate of tetramers formation and enhanced the induction of p53 target expression.
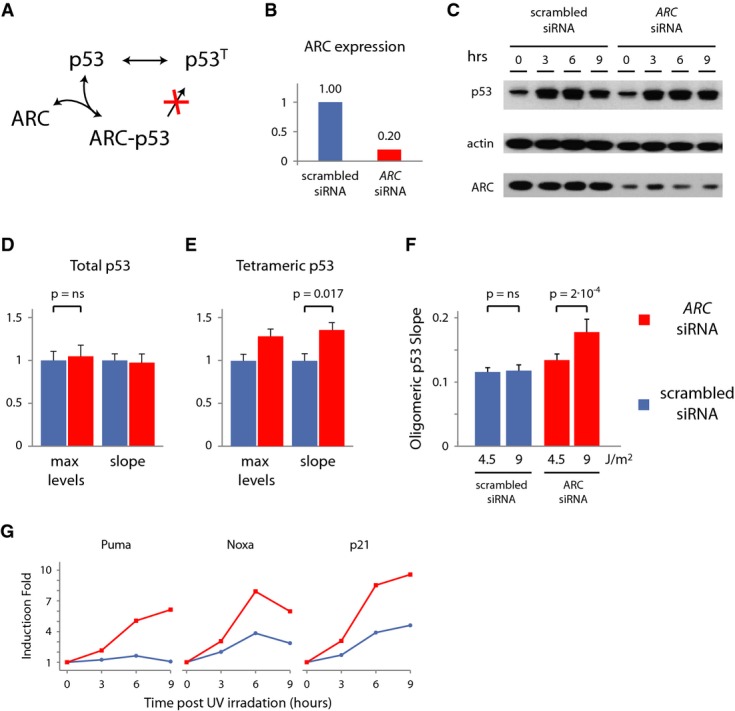
- A The ARC protein binds p53 and interferes with p53 tetramerization.
- B qPCR of ARC mRNA under scrambled and ARC siRNA.
- C Immunoblot of cells following UV at the indicated time points.
- D, E Maximum levels and slope for total (D) and tetrameric (E) p53. Shown are median and SEM. n = 170. ARC knockdown does not affect the total p53 maximum (P = 0.62) and slope (P = 0.57) but increases the rate of p53 tetramer accumulation (P = 0.007 and P = 0.017). P-values were calculated by Mann–Whitney U-test, with P = 0.05 as significance threshold.
- F Knockdown of ARC breaks the slope conservation of tetramers formation. Shown are median and SEM. n = 360. P = 2 × 10−4 for ARC siRNA and P = 0.47 for scrambled siRNA control.
- G Fold induction of p53 target genes quantified by qPCR following 6 J/m2 UV after ARC siRNA (red) or scramble siRNA (blue).
Source data are available online for this figure.
