Figure 2.
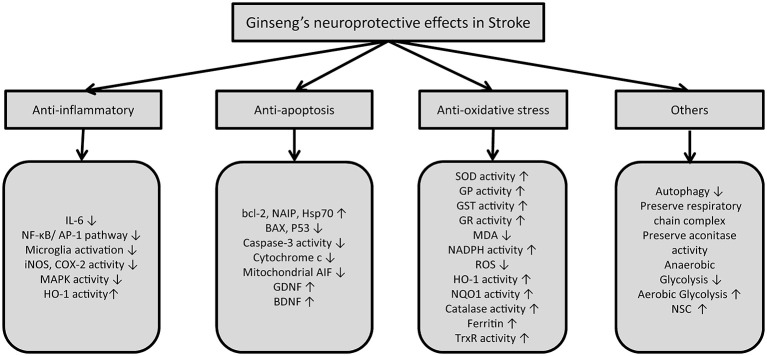
Summary of mechanisms of action of ginseng and its constituents in stroke. (IL-6: Interleukin-6, NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB, AP-1: Activator protein-1, iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase, COX-2: Cycloxygenase-2, MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase, HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1, AIF: apoptosis inducing factor, GDNF: Glial-derived neurotrophic factors, BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, SOD: Superoxide dismutase, GP: Glutathione peroxidase, GST: Glutathione S-transferase, GR: Glutathione reductase, MDA: Malondialdehyde, NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-diaphorase, NQO1: NADPH quinone reductase 1, ROS: Reactive oxygen species, TrxR: Thioredoxin reductase).
