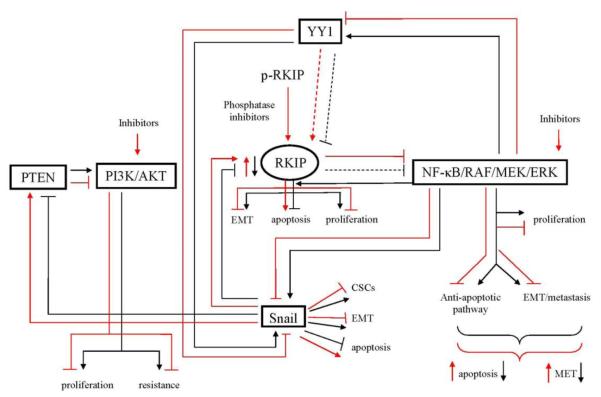
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram demonstrating the role of RKIP in the regulation of tumor cell drug/immune resistance (black lines). Tumor cells exhibit a constitutively hyperactivated NF-κB pathway which regulates, in large part, the survival, growth, metastasis and resistance of tumor cells. Among many target genes that NF-κB regulates, there exists a dysregulated NF-κB/Snail/YY1/PTEN/RKIP loop that is responsible, in part, for NF-κB-mediated above tumor manifestations. The hyperactivated NF-κB pathway regulates cell proliferation, anti-apoptotic pathways, EMT, metastasis and resistance. These events are the results of NF-κB activation of (1) the metastasis inducer and resistance transcription factor Snail, which regulates CSCs, EMT and anti-apoptotic pathways and (2) the drug/immune resistant transcription factor YY1, which also regulates the transcription of Snail. The overexpression of Snail results in the repression of the metastasis suppressor/drug sensitizers, RKIP and PTEN. The repression of RKIP minimally represses the NF-κB pathway directly and indirectly by the repression of PTEN, which does not inhibit the PI3K/AKT pathway that regulates NF-κB. Overall, the tumor cells exhibit a dysregulated NF-κB /Snail/YY1/PTEN/RKIP loop with the overexpression of NF-κB, Snail and YY1 and under expression of RKIP and PTEN and resulting in tumor cell survival, metastasis and drug resistance (red lines). Inhibition of the dysregulated loop products, on each of the overexpressed NF-κB, YY1, Snail, PI3K/AKT, results in the derepression of RKIP and PTEN and resulting in the inhibition of cell growth, survival, EMT, metastasis, and activation of proapoptotic pathways resulting in sensitization to drug-induced apoptosis. There are many classes of inhibitors that may be used and some examples are illustrated in the scheme, for instance, the expression of the active form of RKIP in its phosphorylated form can be rendered active by the use of phosphatase inhibitors. Inhibitors of NF-κB will have both direct and indirect effects on NF-κB target genes such as Snail and YY1 and derepression of RKIP and PTEN. The direct inhibition of Snail and YY1 will have similar effects as the NF-κB inhibitors. Likewise, inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT pathway will have direct and indirect effects on the inhibition of the NF-κB pathway and its targets Snail and YY1.