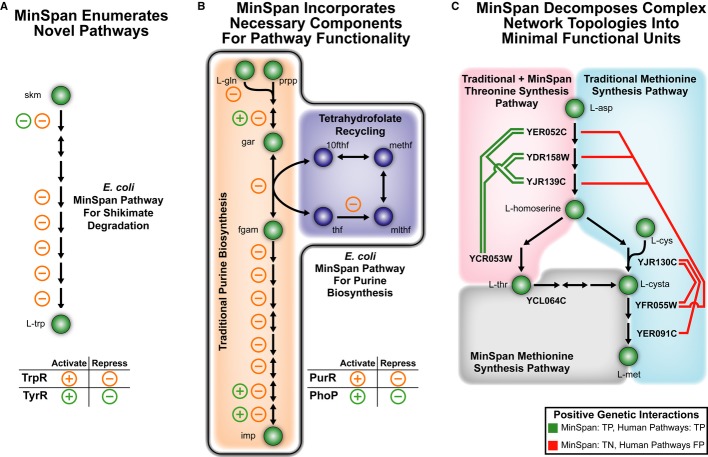
Figure 4. The three differences between MinSpan and human-defined pathways.
- MinSpan automates the enumeration of biologically relevant pathways.
- MinSpan includes all required components of a pathway to be independent. The additional pathway components not found in human-defined pathways, such as THF recycling, are often co-regulated and thus a part of a coherent pathway functioning as a “module” in a network.
- MinSpan decomposes complex topology into the simplest representation. For example, there is a shorter route to l-methionine production through l-threonine than from l-aspartate. Note: For MinSpan pathways, only the representative genes of the pathway are shown. 10fthf: 10-formyltetrahydrofolate; 2obut: 2-oxobutanoate; gar: glycinamide ribonucleotide; l-cysta: l-cystathionine; methf: 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate; mlthf: 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate; prpp: phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate; skm: shikimate; thf: tetrahydrofolate.