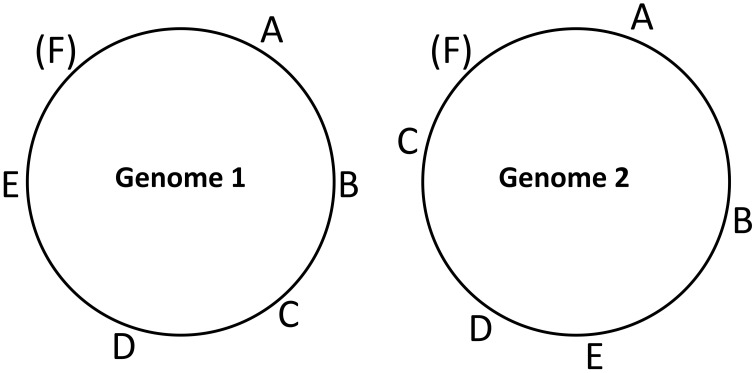
Figure 1.
Diagram demonstrating the method used to calculate the pair wise distributed gene order distance between genomes. Repeatedly, six ortholog pairs are chosen randomly (requiring every gene in the six be at least 5 genes away along the genome from each). The six genes are then tested to see if they are in the same order (irrespective of the orientation of the genes). In the case above, the test fails because orthologs C and E are switched. Distributed gene order distance is equal to the fraction of times such a test fails between two genomes. The diagram also works for demonstrating the distributed gene order distance between genomes using five genes (A–E) by ignoring gene F.