To the Editor:
The Hospital Readmission Reduction Program (HRRP) was established by the Affordable Care Act to improve care quality and reduce hospital spending by penalizing hospitals for “excessive” readmissions rates for common medical conditions (1). At present, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) calculates hospital risk-adjusted readmission rates for acute myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, and pneumonia and penalizes hospitals above the national average up to 2% of their total Medicare reimbursement. Recent data demonstrate that hospitals caring for medically complex and socially vulnerable populations are disproportionately penalized under the HRRP (2).
Beginning in 2015, CMS will add chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to the list of penalized conditions and will increase the maximum penalty to 3% of total reimbursement for hospitals with excessive readmissions (3). Exacerbations of COPD disproportionately affect minorities and individuals of lower socioeconomic status (SES) (4). Whether adding COPD readmissions to the HRRP will further hurt hospitals caring for such patients is unknown. Our aim in this study was to determine the relationship between COPD readmission rates and two hospital characteristics: hospital teaching status and the SES of the hospital’s patient population. We hypothesized that hospitals caring for a high percentage of patients of low SES and teaching hospitals would be those most likely penalized for high COPD readmission rates under the HRRP.
Methods
We used publically reported data from the HRRP supplemental file for 2015, which includes risk-standardized COPD readmission ratios for each hospital (5). We multiplied each hospital’s ratio by 22.1%, the national readmission rate for COPD in the Medicare population, to calculate COPD readmission rates at each hospital. We grouped hospitals into quartiles by readmission rates and linked these hospital-level data to hospital characteristics available in the Healthcare Cost Report and Information System (6). We defined teaching status as hospitals with no residents, fewer than 0.25 full-time equivalent (FTE) residents per bed, or greater than 0.25 FTE residents/bed. We defined hospitals with a high proportion of low-SES status patients as those in the highest quartile of disproportionate share patient percentage, a measure used by CMS to quantify care provided to the poor (7).
We compared hospital characteristics across COPD readmission rate quartile, using chi-squared tests. We entered teaching status and the SES status of the hospital’s patients into a single multivariable ordinal logistic regression model to determine their association with a higher quartile of COPD readmission rate. We adjusted the model for profit status, bed number, and volume of COPD admissions. We included those hospital characteristics as potential confounders because of their potential association with readmission rates. Finally, we estimated COPD readmission rates across Hospital Referral Regions by averaging hospital rates within each region weighted by volume and grouped referral regions into quartiles. All data management and analysis was conducted using Stata 13 (StataCorp, College Station, TX). Our study received an exemption from our institutional review board because of our use of public data.
Results
Data were available from 3,018 hospitals. COPD readmission rates ranged from 17% to 28% across hospitals. Hospitals with higher readmission rates were more often high-volume centers, major teaching hospitals, and hospitals with a high proportion of low-SES-status patients (in the highest quartile of disproportionate share patient percentage; Table 1). After adjusting for all other characteristics, major teaching hospital status (odds radio [OR], 1.85; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.44–2.39), highest quartile of low-SES patients (OR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.15–1.74), and highest quartile of COPD volume (OR, 2.35; 95% CI, 1.85–2.99) were all characteristics independently associated with being in a higher quartile of COPD readmission rate (P < 0.001 for all). COPD readmission rates were greatest in the Mid-Atlantic, Midwest, and South relative to other regions (Figure 1).
Table 1.
Characteristics of Hospitals with Varying COPD Readmission Rates
| Hospital Quartile of COPD Readmission Rate |
P Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartile 1 (N = 757) (%) | Quartile 2 (N = 753) (%) | Quartile 3 (N = 752) (%) | Quartile 4 (N = 756) (%) | ||
| COPD readmission rates | 17–21 | 21–22 | 22–23 | 23–28 | |
| Hospital characteristics | |||||
| Ownership | <0.001 | ||||
| Nonprofit | 68.0 | 58.6 | 58.5 | 61.5 | |
| Profit | 17.0 | 23.1 | 25.3 | 23.7 | |
| Government | 14.9 | 18.3 | 16.2 | 14.8 | |
| Hospital beds | 0.08 | ||||
| <200 | 69.1 | 70.7 | 71.9 | 65.5 | |
| 200–399 | 23.7 | 23.6 | 20.9 | 25.8 | |
| >400 | 7.3 | 5.7 | 7.2 | 8.7 | |
| COPD volume (quartiles) | <0.001 | ||||
| Lowest (<38 per year) | 19.3 | 28.3 | 29.5 | 10.6 | |
| Second (38–77) | 28.7 | 25.9 | 25.0 | 24.2 | |
| Third (78–133) | 27.1 | 25.2 | 24.3 | 27.7 | |
| Highest (134–920) | 25.0 | 20.6 | 21.1 | 37.6 | |
| Teaching status | <0.001 | ||||
| None | 69.0 | 69.5 | 69.2 | 64.4 | |
| Minor teaching | 23.7 | 19.5 | 17.0 | 20.2 | |
| Major teaching | 7.4 | 11.0 | 13.8 | 15.3 | |
| DSH patient percentage | 0.01 | ||||
| Lowest quartile | 28.0 | 25.9 | 22.4 | 22.8 | |
| Second quartile | 32.2 | 35.0 | 36.3 | 29.2 | |
| Third quartile | 17.5 | 15.8 | 15.9 | 17.9 | |
| Highest quartile | 22.3 | 23.3 | 25.5 | 30.1 | |
Definition of abbreviations: COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; DSH = disproportionate share.
All numbers are percentages. P values are from chi-squared analysis. Minor teaching includes less than 0.25 full-time equivalent residents/hospital bed; major teaching includes greater than 0.25 full-time equivalent/bed. DSH patient percentage is a measure used by CMS to quantify care provided to the poor, calculated as follows: (patient-days of Medicare and supplemental security income eligible patients)/(total Medicare patient-days) + (Medicaid, non-Medicare patient-days)/(total patient-days).
Figure 1.
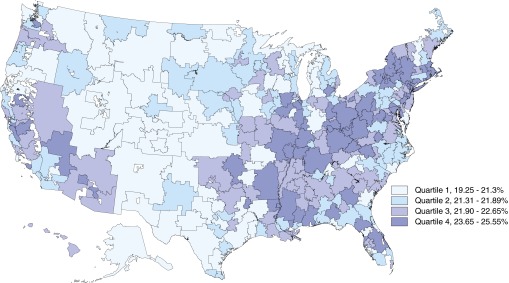
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease readmission rates across hospital referral regions. Rates were calculated by averaging hospital rates within each region weighted by volume, and referral regions were grouped into quartiles.
Discussion
We found that high-volume hospitals, major teaching hospitals, and hospitals with the highest percentage of low-SES patients were more often among hospitals with high COPD readmission rates. In addition, geographic areas often with a greater burden of low-income patients also had higher COPD readmission rates. These data suggest that hospitals caring for disadvantaged populations are more likely to be penalized for high COPD readmission rates.
Prior work demonstrates that readmission penalties for congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and pneumonia disproportionately affect hospitals caring for vulnerable patient populations. Penalties for COPD target the same hospitals, suggesting that inclusion of the disease in the HRRP will increase the hospitals’ financial losses and further deplete their limited resources. The HRRP encourages hospitals to reduce readmissions by improving inpatient care and care transitions. However, no interventions to date have been shown to reliably reduce COPD readmission rates (8). Moreover, patient factors linked to socioeconomic resources (social support, stable housing, and access to care) often contribute to readmissions (9, 10).
A National Quality Forum working group convened at the request of the federal government recently recommended that CMS include socioeconomic factors in the risk adjustment of hospital performances measures (11). Whether CMS will adopt this recommendation and whether the new adjustment methods will be adequate remains unclear. For now, hospitals caring for socially vulnerable patients will continue to receive penalties for factors outside their control.
Footnotes
The authors are supported by grant T32HL007749 from the National Institutes of Health (M.W.S.) and grant K08HS020672 from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (C.R.C.).
Author Contributions: M.W.S. had full access to the data and takes responsibility for the data integrity and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study concept and design: both authors; acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: both authors; drafting of the manuscript: M.W.S.; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: both authors; statistical analysis: M.W.S.; obtained funding: both authors; study supervision: C.R.C.
Author disclosures are available with the text of this letter at www.atsjournals.org.
References
- 1.James J.Medicare hospital readmission reduction program Bethesda, MD: Health Affairs; November 12, 2013[accessed 2014 Jun 18]. Available from: http://www.healthaffairs.org/healthpolicybriefs/brief.php?brief_id=102 [Google Scholar]
- 2.Joynt KE, Jha AK. Characteristics of hospitals receiving penalties under the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program. JAMA. 2013;309:342–343. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.94856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Feemster LC, Au DH. Penalizing hospitals for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease readmissions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;189:634–639. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201308-1541PP. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Eisner MD, Blanc PD, Omachi TA, Yelin EH, Sidney S, Katz PP, Ackerson LM, Sanchez G, Tolstykh I, Iribarren C. Socioeconomic status, race and COPD health outcomes. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2011;65:26–34. doi: 10.1136/jech.2009.089722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Readmissions reduction program Baltimore, MD: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services; [updated 2014 Aug 4; accessed 2014 July 15]. Available from: http://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/AcuteInpatientPPS/Readmissions-Reduction-Program.html [Google Scholar]
- 6.Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Hospital cost report Baltimore, MD: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services; [updated 2013 May 7; accessed 2014 Jan 4]. Available from: http://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Files-for-Order/CostReports/Cost-Reports-by-Fiscal-Year.html [Google Scholar]
- 7.Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Disproportionate share hospital Baltimore, MD: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services; [updated 2014 Aug 4; accessed 2014 Jul 15]. Available from: http://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/AcuteInpatientPPS/dsh.html [Google Scholar]
- 8.Prieto-Centurion V, Markos MA, Ramey NI, Gussin HA, Nyenhuis SM, Joo MJ, Prasad B, Bracken N, Didomenico R, Godwin PO, et al. Interventions to reduce rehospitalizations after chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations: a systematic review. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014;11:417–424. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201308-254OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Calvillo-King L, Arnold D, Eubank KJ, Lo M, Yunyongying P, Stieglitz H, Halm EA. Impact of social factors on risk of readmission or mortality in pneumonia and heart failure: systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2013;28:269–282. doi: 10.1007/s11606-012-2235-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Prieto-Centurion V, Gussin HA, Rolle AJ, Krishnan JA. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease readmissions at minority-serving institutions. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013;10:680–684. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201307-223OT. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.National Quality Forum Risk adjustment for sociodemographic factors Washington, DC: National Quality Forum; 2014. [accessed 2014 Aug 17]. Available from: http://www.qualityforum.org/risk_adjustment_ses.aspx [Google Scholar]


